ACP C++
Overview
In this manual, SX20 is used as ACP server and Ubuntu computer is used as the client to read, write, and subscribe to PLC variable functions. It is shown in the figure below:
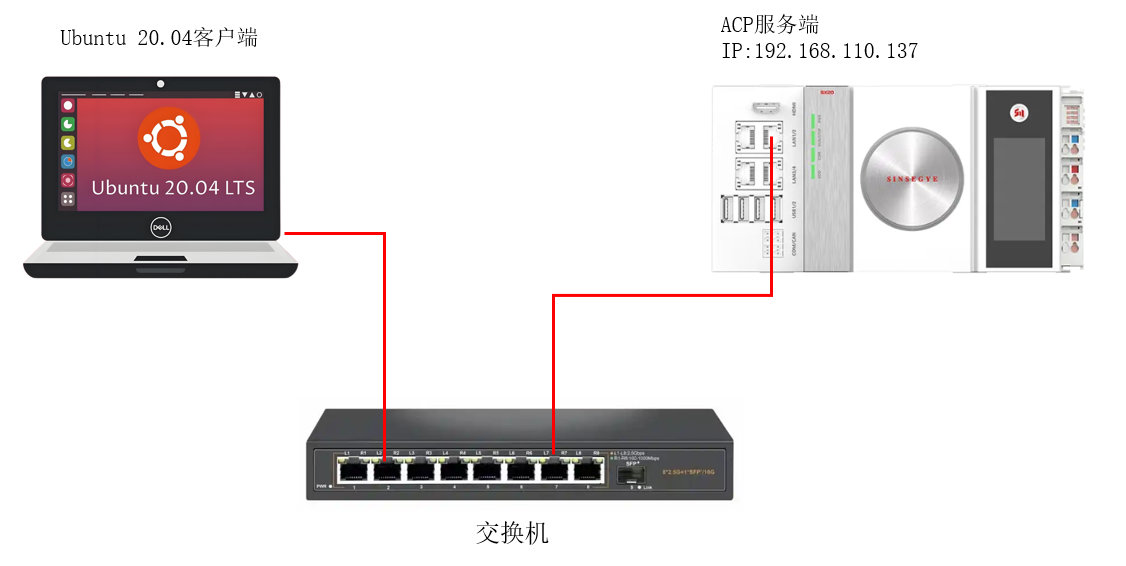
The following table provides an overview of the product components in this manual
| Product Components | Description |
|---|---|
| acpplcaccess_0.1.5-rc.3_amd64.deb | The deb component for iComputer ACP Server |
| acpsymbollib_0.0.5-rc.2_amd64.deb | The deb component for Ubuntu Client |
| liblibacp.so | libacp dependency file |
| CppAcpServer.projectarchive | PLC Project Archive |
| AcpClient.cpp | Linux Client C++ Example Program |
Download:ACP.ZIP
Install and Uninstall
I. Installation Requirements
-
Self-contained system of the iComputer produced by Sinsegye;
-
iComputer can access the internet;
-
The Ubuntu system client can access the Internet;
II. Installation Process
1. Install the deb component on the iComputer
Refer to Appendix I. Use Windows cmd to input the command, and then install acpplcaccess_0.1.5-rc.3_amd64.deb file downloaded from official website to the iComputer.
scp -P 2224 acpplcaccess_0.1.5-rc.3_amd64.deb sinsegye@192.168.110.137:~
ssh -p 2224 sinsegye@192.168.110.137
sudo dpkg -i acpplcaccess_0.1.5-rc.3_amd64.deb
Or carry out force installation of sudo dpkg -i --force-overwrite acpplcaccess_0.1.5-rc.3_amd64.deb
sudo nano /usr/local/etc/SinsegyeRTE/SinsegyeRTE.cfg
Modify ComponentManager
sudo reboot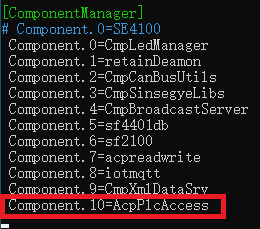
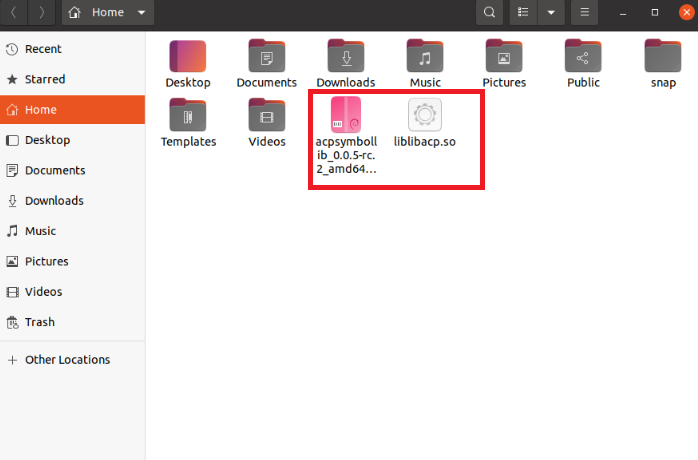
2. Install acpsymbollib_0.0.5-rc.2_amd64.deb and the dependency file liblibacp.so on the Ubuntu 20.04 computer.
Copy the acpsymbollib_0.0.5-rc.2_amd64.deb and liblibacp.so downloaded from the official website to the folder Ubuntu client/home.
Open Ubuntu terminal and install acpsymbollib_0.0.5-rc.2_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i acpsymbollib_0.0.5-rc.2_amd64.deb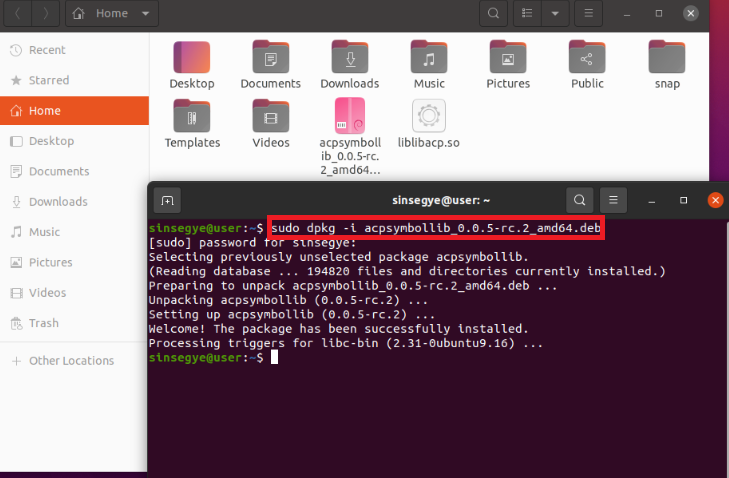
Copy liblibacp.so to the folder /usr/lib/
sudo cp liblibacp.so /usr/lib/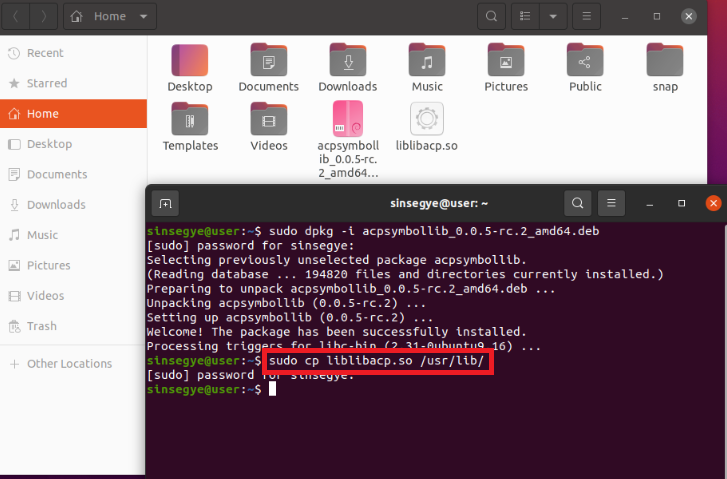
3. Install VScode on Ubuntu.
Use Ubuntu Sofware to install VScode. If there is no Ubuntu-soft, download it by using the command first.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt -y install ubuntu-software
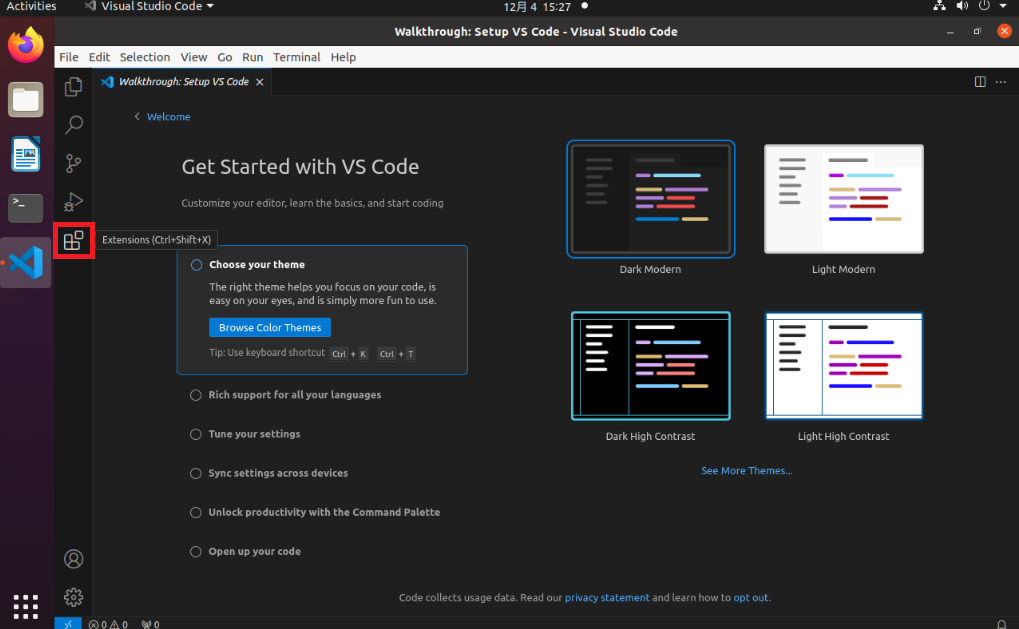
Open VScode and click "Extensions".
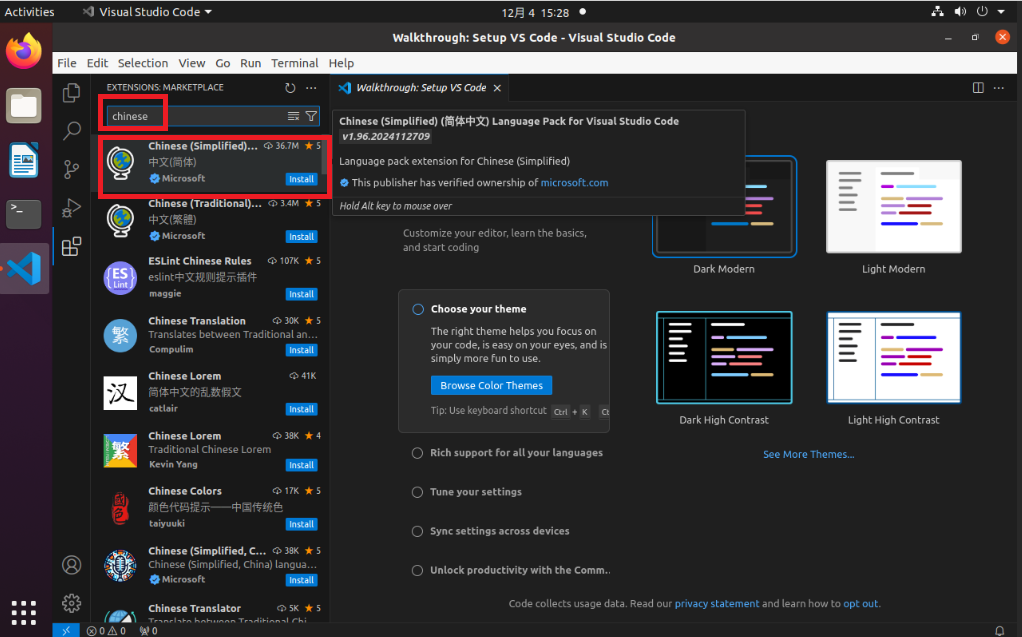
Search for "Chinese" - select Chinese (simplified) - install
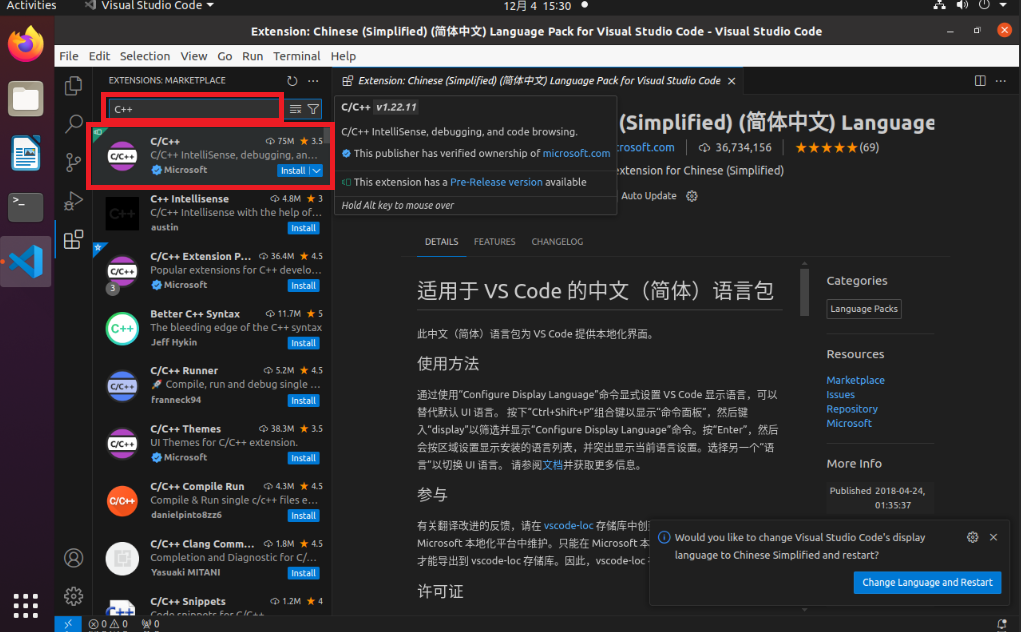
Search for "C++" - Click Install
Restart the Ubuntu system.
4. Set VScode C++ compilation environment
Open the VScode software on Ubuntu and click "Select My Default Editor"
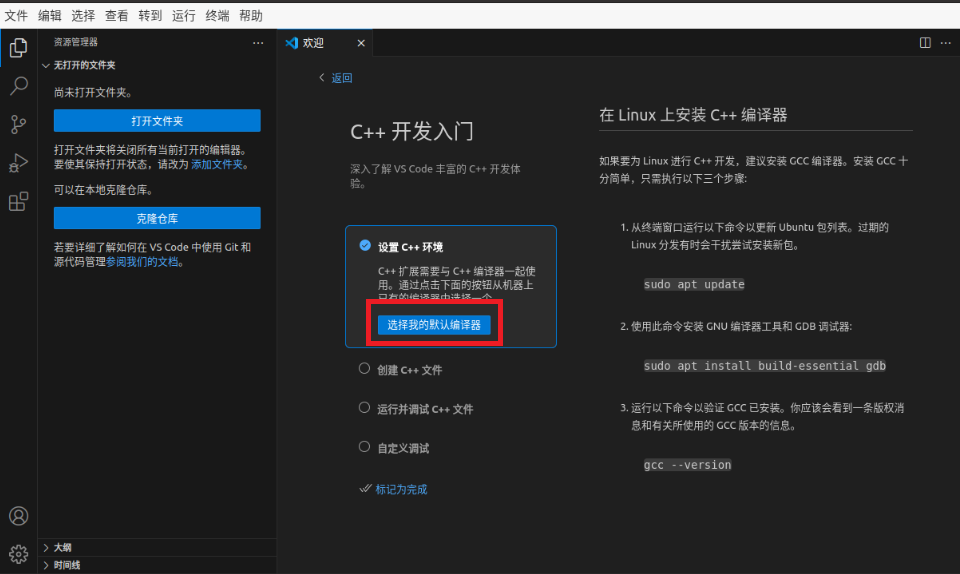
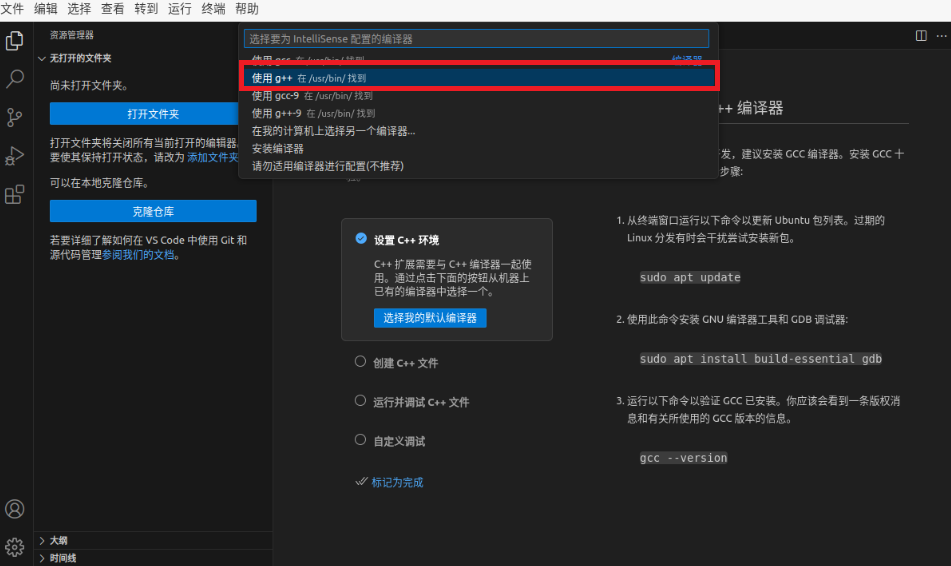
Choose to use the g++ compiler
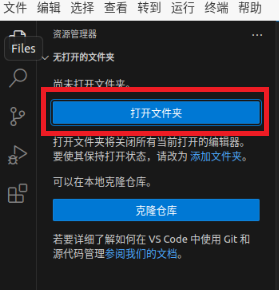
Click on “Open Folder”
Create a new folder
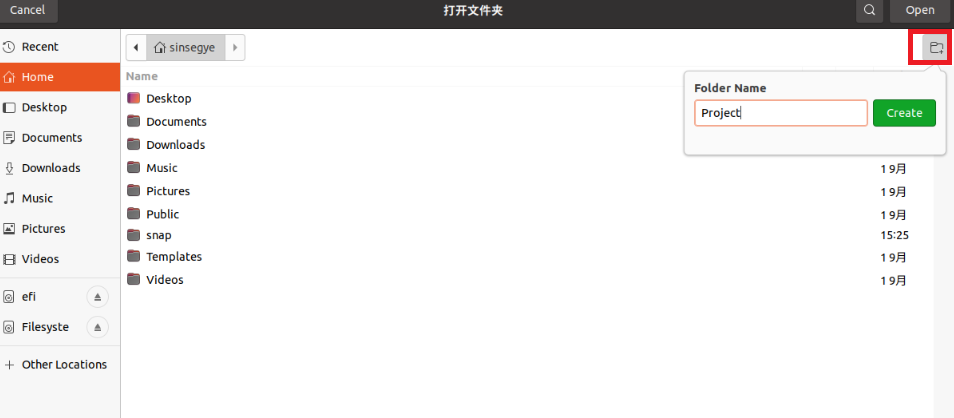
Click “OPEN”
Click “Yes, I trust the author”
Create a new cpp file
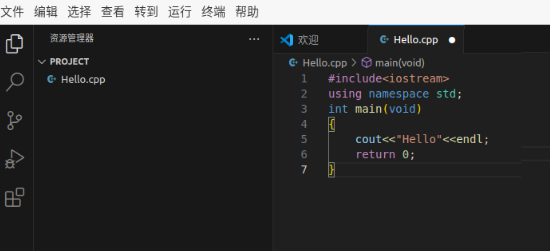
Write a test program
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
cout<<"Hello"<<endl;
return 0;
}
Click “Terminal” – “Configure Default Generation Task”
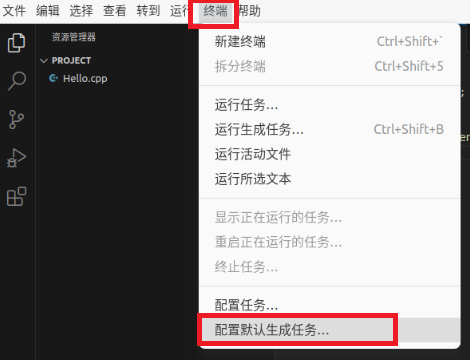
Select "g++ Generate Active File"
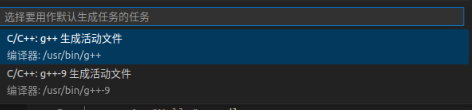
Add “-lacpsymbollib”,
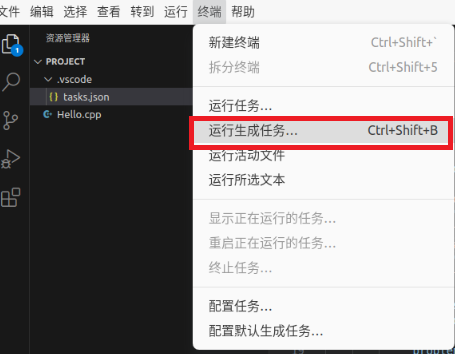
Click “Run the Generated Task
Click “Run” – “Add Configuration”
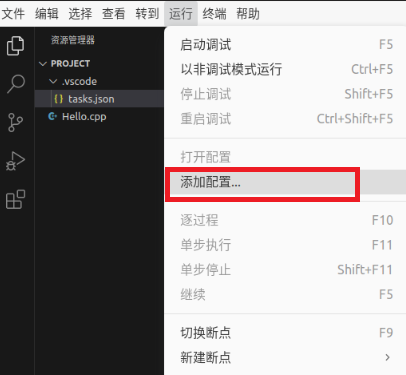
Select "C++"
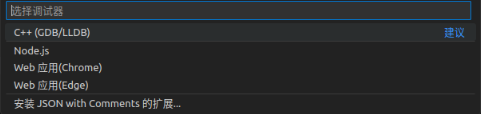
Click “Add Configuration” – “(gdb) Startup”
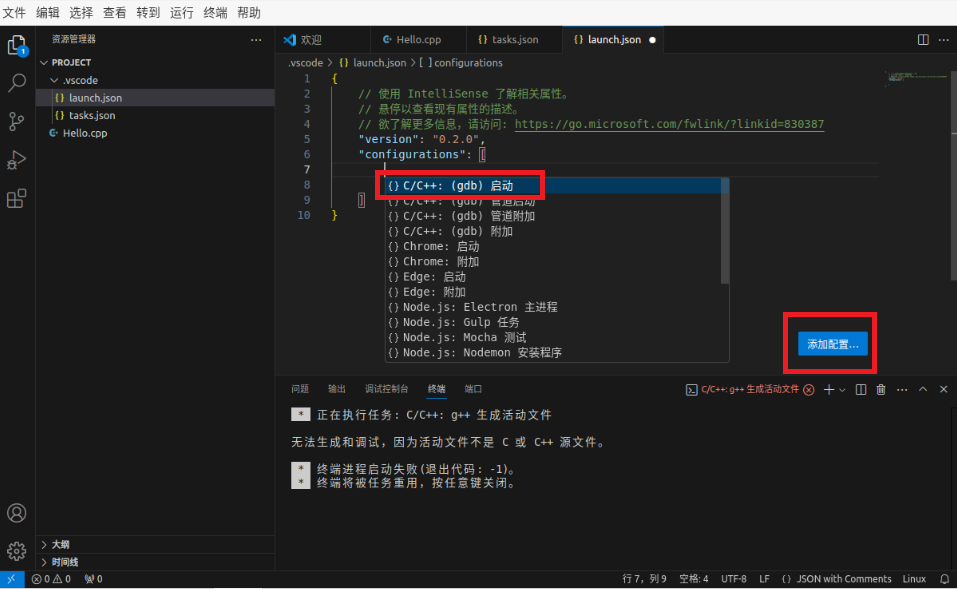
Modify the "program" parameter to "{fileDirname}/{fileBasenameNoExtension}"
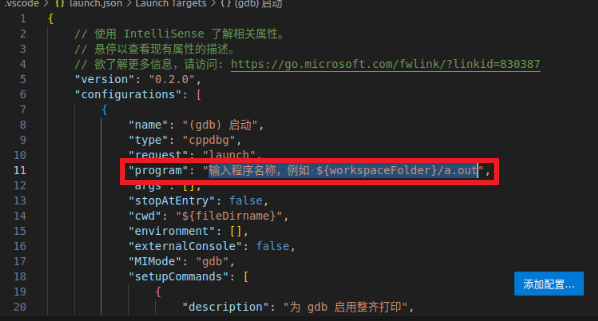
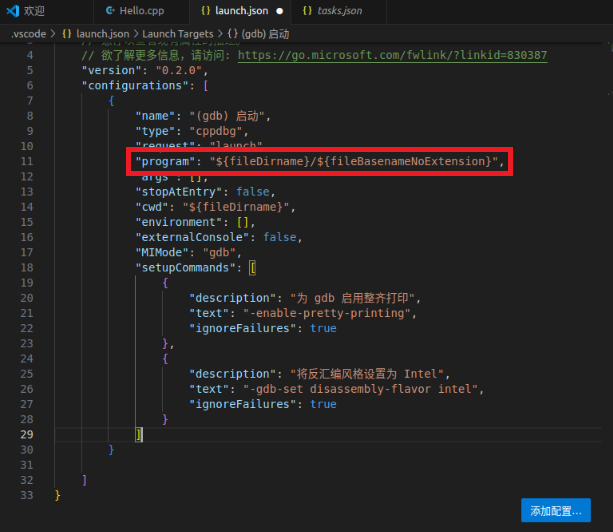
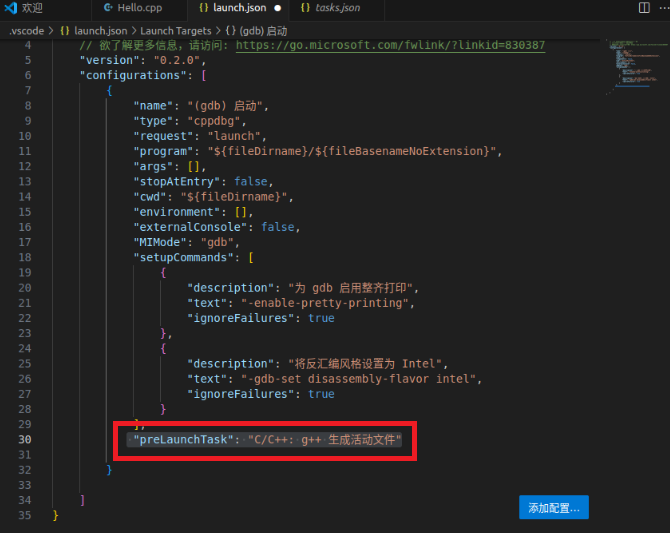
Also add the attribute "preLaunchTask": "C/C++: g++ Generate Active File"
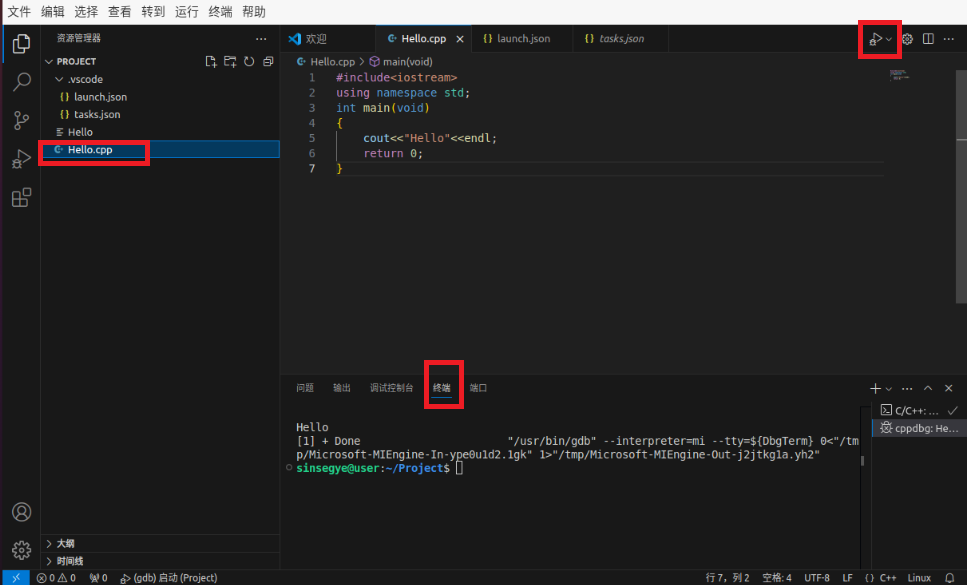
Select Hello.cpp - debug, and you can see the debug results on the terminal.
III. Updating and Installation
Refer to the previous chapter II. Installation Process. The new deb file and dependency file can be updated by overwriting the installation.
IV. Uninstall Process
1. Uninstall the deb component from the iComputer
1.1 Uninstall it by using the dpkg -r command
sudo dpkg -r acpplcaccess1.2 Modify the configuration file of RTE, and delete AcpPlcAccess from the ComponentManger module.
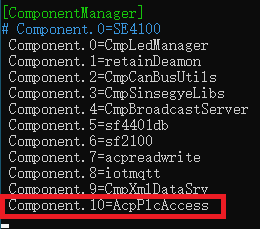
sudo nano /usr/local/etc/SinsegyeRTE/SinsegyeRTE.cfgDelete Component.10=AcpPlcAccess
1.3 Restart the iComputer
sudo reboot2. Uninstall the deb component acpsymbollib from the Ubuntu Client
2.1 Uninstall it by using the dpkg -r command
sudo dpkg -r acpsymbollib2.2 Restart
sudo reboot3. Uninstall VScode from the Ubuntu Client
Uninstall VScode by using Ubuntu-Software
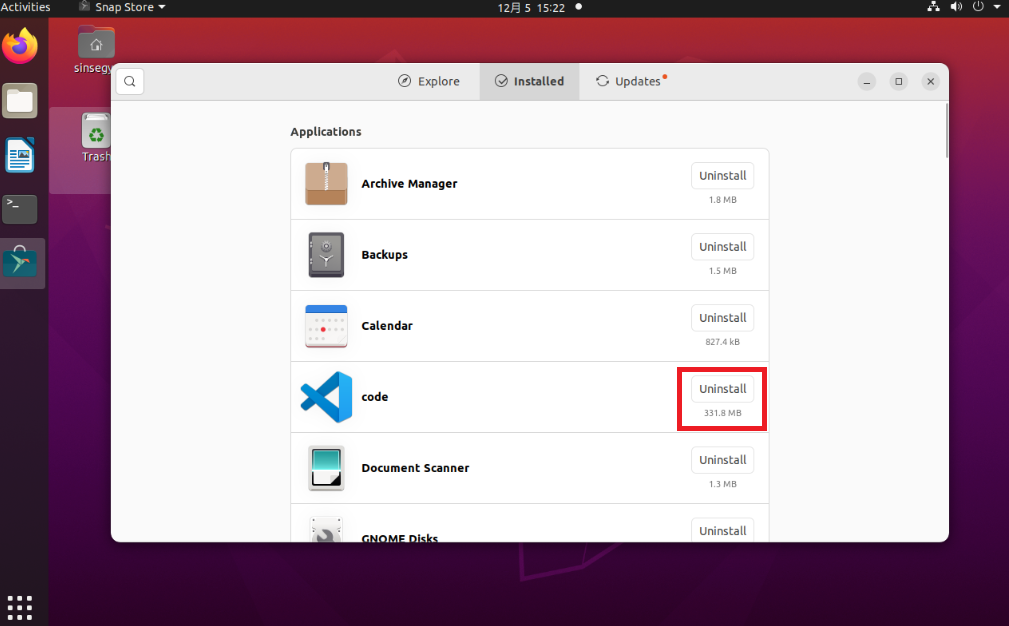
Technical Description
I. Quick Start
(I) Software and hardware configurations of this example
| Hardware: | Software: |
|---|
(II) Experimental operation steps of this example
1. Experimental requirements
a. Successfully install the acpplcaccess_0.1.5-rc.3_amd64.deb component on the iComputer;
b. Install acpsymbollib_0.0.5-rc.2_amd64.deb and liblibacp.so on the Linux System Client;
c. Install the VScode software on the Linux System Client and configure the C++ compilation environment.
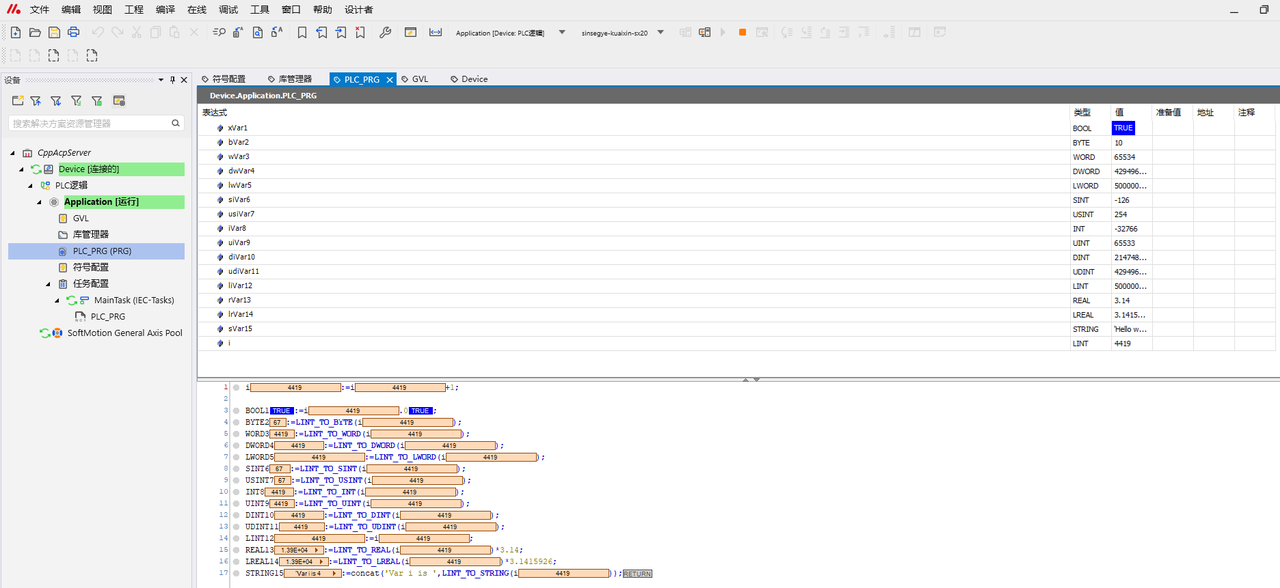
2. Schematic diagram of the experiment
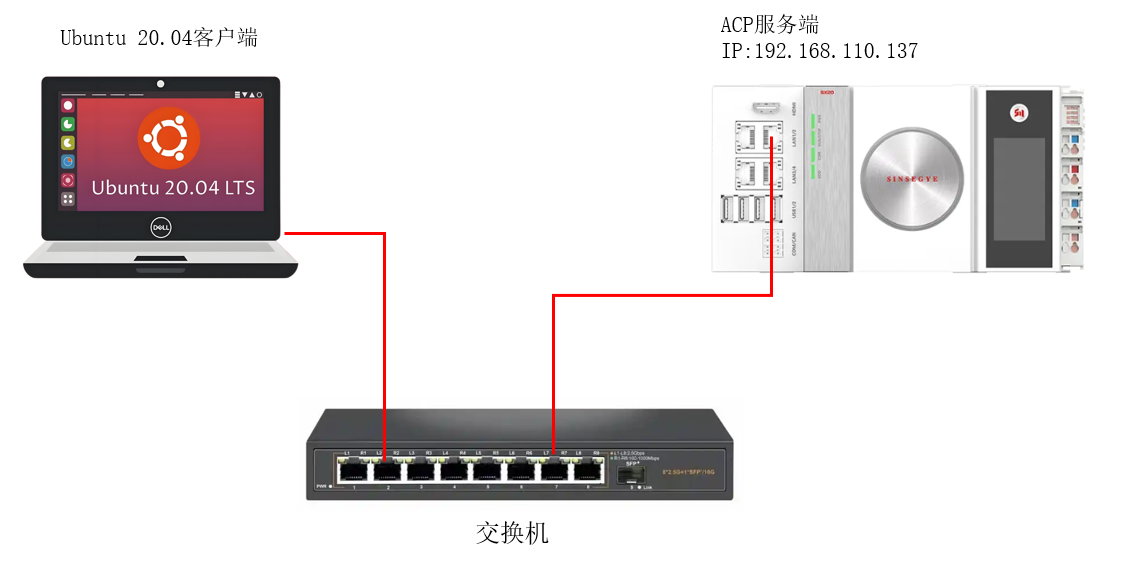
3. Experimental steps
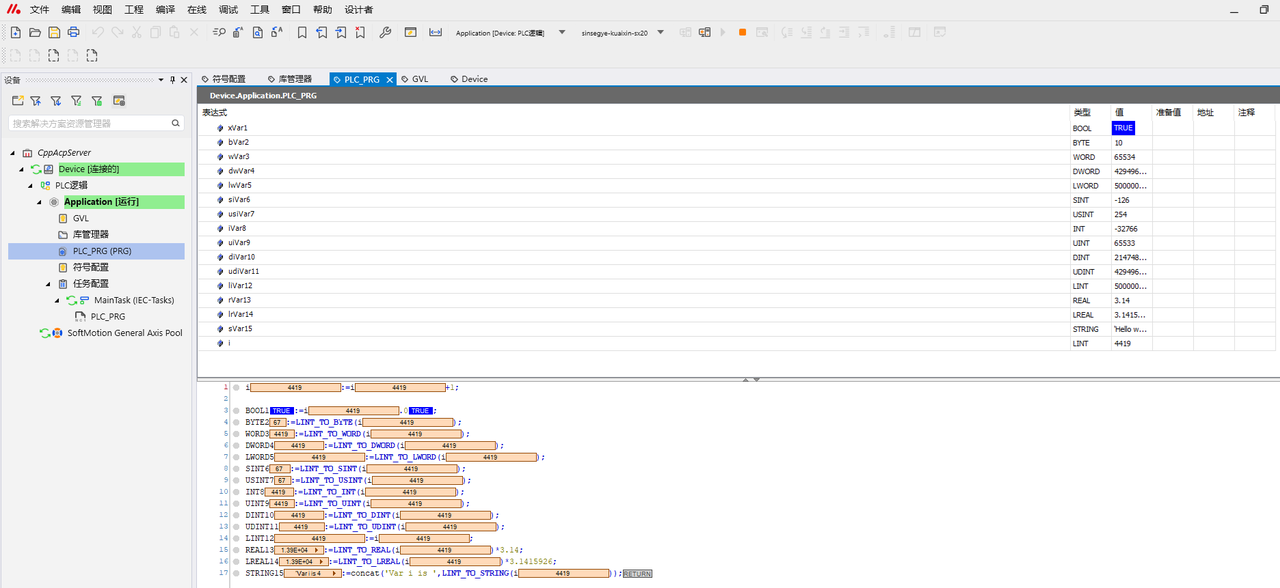
3.1 Unzip the project archive file “CppAcpServer.projectarchive” downloaded from the official website, log in the iComputer, and download the Run program.
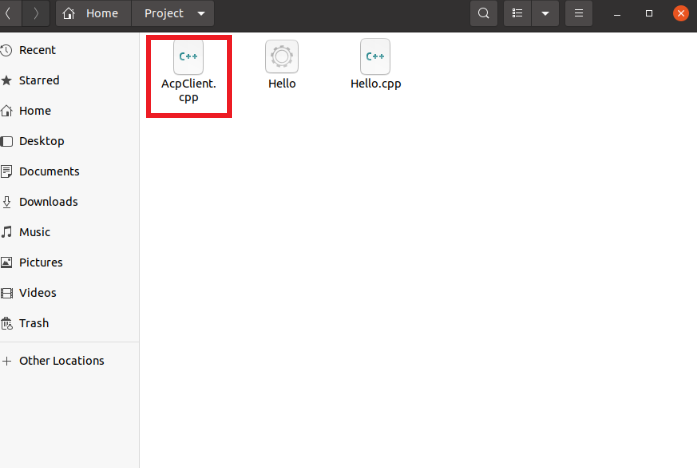
3.2 Copy the C++ program “AcpClient.cpp” downloaded from the official website to the Project folder of Ubuntu.
3.3 Select the program AcpClient.cpp in VScode, and uncomment ReadSymbol() in main() function.
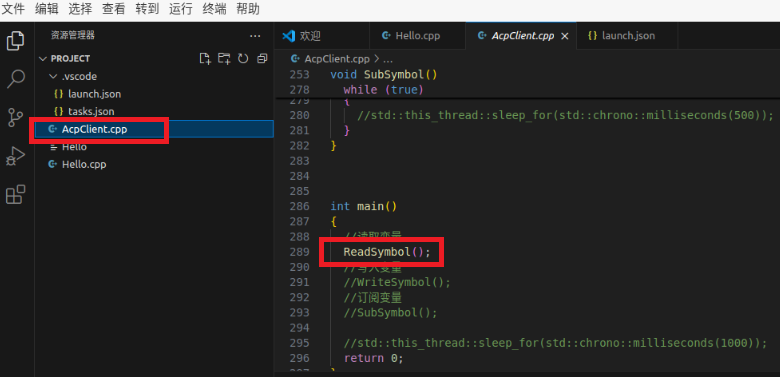
3.4 Click Debug to read variables in PLC_PRG
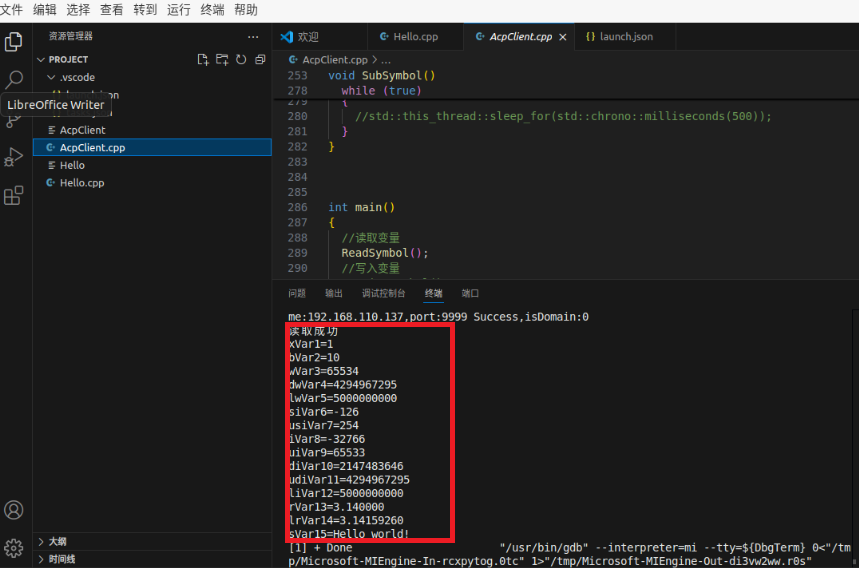
3.5 Comment ReadSymbol() and uncomment Writesymbol() in main() function. Click Debug to write the variable value.
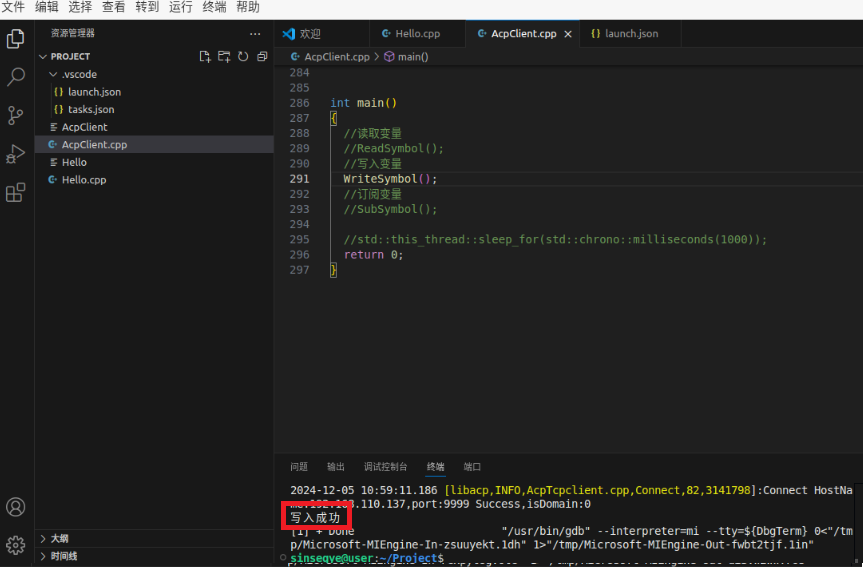
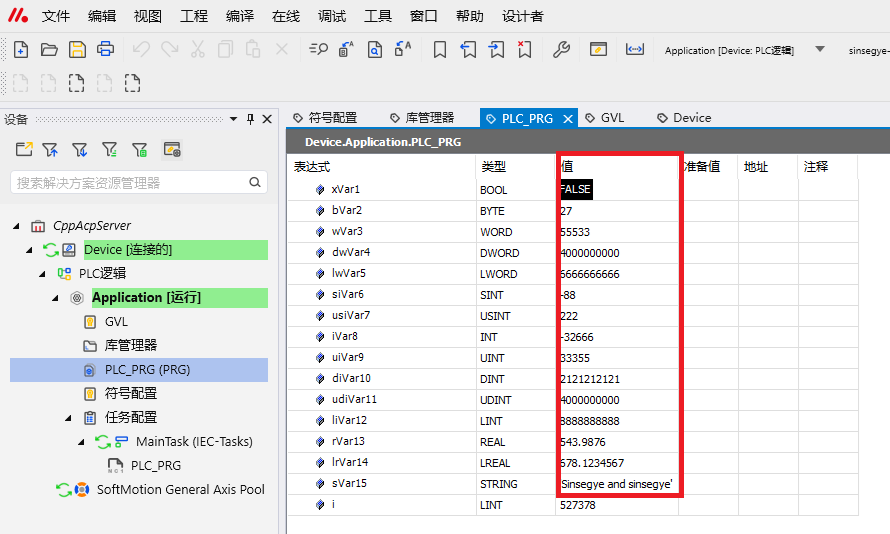
Check the PLC variable value of the iComputer and write it successfully.
3.6 Comment Writesymbol() and uncomment SubSymbol() in main() function. Click Debug to subscribe to variables.
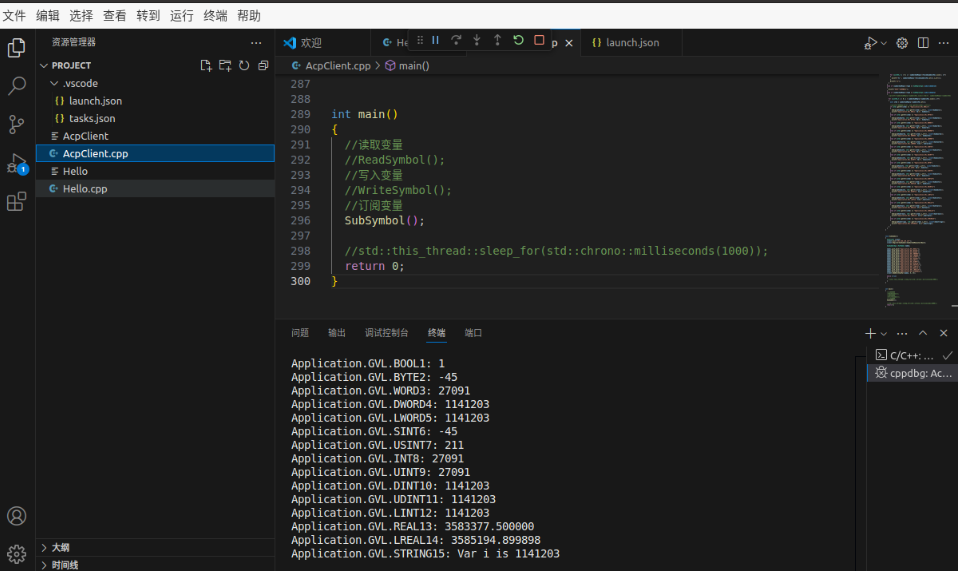
The values of the subscribed variables are constantly changing.
II. Example
Read Variable
Use client. Init() to connect the server.
Define the varmap type to represent mapping a string into the VarPair data structure to manage the symbol address and size. Create the string by using char string\[].
Use client.ReadSymbols() to read variables.
See Function Introduction for detailed parameter description.
void ReadSymbol() {
AcpClient client; //Create a client
client.Init("192.168.110.137"); //Connect the server
AcpSymbolApi::VarMap varmap;
BOOL bool1=false;
BYTE byte1=0;
WORD word1=0;
DWORD dword1=0;
LWORD lword1=0;
SINT sint1=0;
USINT usint1=0;
INT int1= 0;
UINT uint1=0;
DINT dint1=0;
UDINT udint1=0;
LINT lint1=0;
REAL real1= 0;
LREAL lreal1=0;
char string1[80] = "";
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.xVar1"] = std::make_pair(&bool1, sizeof(BOOL));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.bVar2"] = std::make_pair(&byte1, sizeof(BYTE));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.wVar3"] = std::make_pair(&word1, sizeof(WORD));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.dwVar4"] = std::make_pair(&dword1, sizeof(DWORD));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.lwVar5"] = std::make_pair(&lword1, sizeof(LWORD));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.siVar6"] = std::make_pair(&sint1, sizeof(SINT));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.usiVar7"] = std::make_pair(&usint1, sizeof(USINT));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.iVar8"] = std::make_pair(&int1, sizeof(INT));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.uiVar9"] = std::make_pair(&uint1, sizeof(UINT));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.diVar10"] = std::make_pair(&dint1, sizeof(DINT));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.udiVar11"] = std::make_pair(&udint1, sizeof(UDINT));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.liVar12"] = std::make_pair(&lint1, sizeof(LINT));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.rVar13"] = std::make_pair(&real1, sizeof(REAL));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.lrVar14"] = std::make_pair(&lreal1, sizeof(LREAL));
varmap["Application.PLC_PRG.sVar15"] = std::make_pair(&string1,sizeof(string1));
auto result = client.ReadSymbols(varmap);
if (result != true)
{
printf("Read failed\n");
}
else
{
printf("Read succeeded\n");
printf("xVar1=%d\n",bool1);
printf("bVar2=%d\n",byte1);
printf("wVar3=%d\n", word1);
printf("dwVar4=%u\n",dword1);
printf("lwVar5=%ld\n",lword1);
printf("siVar6=%d\n",sint1);
printf("usiVar7=%d\n",usint1);
printf("iVar8=%d\n",int1);
printf("uiVar9=%d\n",uint1);
printf("diVar10=%d\n",dint1);
printf("udiVar11=%u\n",udint1);
printf("liVar12=%ld\n",lint1);
printf("rVar13=%f\n",real1);
printf("lrVar14=%.8lf\n",lreal1);
printf("sVar15=%s \n",string1);
}
}Write Variable
Write variables by using client.WriteSymbols().
Use STRING_<N> type of the string.
See Function Introduction for detailed parameter description.
oid WriteSymbol() {
AcpClient client;
client.Init("192.168.110.137");
AcpSymbolApi::VarMap Writevarmap;
BOOL bool1=false;
BYTE byte1=27;
WORD word1=55533;
DWORD dword1=4000000000;
LWORD lword1=6666666666;
SINT sint1=-88;
USINT usint1=222;
INT int1= -32666;
UINT uint1=33355;
DINT dint1=2121212121;
UDINT udint1= 4000000000;
LINT lint1=8888888888;
REAL real1= 543.9876;
LREAL lreal1=678.1234567;
STRING_<80> string1="Sinsegye and sinsegye";
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.xVar1"] = std::make_pair(&bool1, sizeof(BOOL));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.bVar2"] = std::make_pair(&byte1, sizeof(BYTE));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.wVar3"] = std::make_pair(&word1, sizeof(WORD));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.dwVar4"] = std::make_pair(&dword1, sizeof(DWORD));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.lwVar5"] = std::make_pair(&lword1, sizeof(LWORD));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.siVar6"] = std::make_pair(&sint1, sizeof(SINT));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.usiVar7"] = std::make_pair(&usint1, sizeof(USINT));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.iVar8"] = std::make_pair(&int1, sizeof(INT));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.uiVar9"] = std::make_pair(&uint1, sizeof(UINT));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.diVar10"] = std::make_pair(&dint1, sizeof(DINT));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.udiVar11"] = std::make_pair(&udint1, sizeof(UDINT));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.liVar12"] = std::make_pair(&lint1,sizeof(LINT));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.rVar13"] = std::make_pair(&real1,sizeof(REAL));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.lrVar14"] = std::make_pair(&lreal1,sizeof(LREAL));
Writevarmap["Application.PLC_PRG.sVar15"] = std::make_pair(&string1,sizeof(string1));
auto result = client.WriteSymbols(Writevarmap);
if (result != true)
{
printf("Write failed\n");
}
else
{
printf("Write succeeded\n");
}
}Subscribe to Variable
Register a subscription by using client.RegisterSubSymbol();
Add a subscription by using client.AddBatchSubVar();
See Function Introduction for detailed parameter description.
void SubSymbol()
{
AcpClient client;
client.Init("192.168.110.137");
client.RegisterSubSymbol(SymbolSubReplyCallBack); //Register callback function
AcpSymbolApi::VarNames names;
names.push_back("Application.GVL.BOOL1");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.BYTE2");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.WORD3");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.DWORD4");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.LWORD5");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.SINT6");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.USINT7");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.INT8");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.UINT9");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.DINT10");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.UDINT11");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.LINT12");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.REAL13");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.LREAL14");
names.push_back("Application.GVL.STRING15");
client.AddBatchSubVar(names, 6, 15);
while (true)
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(500));
}
}Callback function
void SymbolSubReplyCallBack(SymbolSubReply* symbolSubReply) {
//printf("SymbolSubReplyCallBack in:%d\n", symbolSubReply->type);
int64_t subid=symbolSubReply->subid; //Subid is required for unsubscription
BOOL Subbool1=false;
BYTE Subbyte1=0;
WORD Subword1=0;
DWORD Subdword1=0;
LWORD Sublword1=0;
SINT Subsint1=0;
USINT Subusint1=0;
INT Subint1= 0;
UINT Subuint1=0;
DINT Subdint1=0;
UDINT Subudint1=0;
LINT Sublint1=0;
REAL Subreal1= 0;
LREAL Sublreal1=0;
char Substring1[80]="";
if (symbolSubReply->type == SubReplyType::subscribefailed)
{
printf("Subscription failed\n");
if (symbolSubReply->faliedsymbolsVec.size() > 0)
{
printf("Failed variable: ");
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < symbolSubReply->faliedsymbolsVec.size(); i++)
{
printf("%s ", symbolSubReply->faliedsymbolsVec.at(i).c_str());
}
printf("\n");
}
}
else if (symbolSubReply->type == SubReplyType::subscribedelok)
{
printf("Unsubscription succeeded\n");
}
else if (symbolSubReply->type == SubReplyType::subscribedata)
{
//printf("symbolSubReply->symbolsVec.size():%ld\n", symbolSubReply->symbolsVec.size());
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < symbolSubReply->symbolsVec.size(); i++)
{
auto item = symbolSubReply->symbolsVec.at(i);
//printf("variable name: %s\n", std::get<0>(item).c_str());
if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.BOOL1")
{
memcpy(&Subbool1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subbool1));
printf("Application.GVL.BOOL1: %d\n", Subbool1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.BYTE2")
{
memcpy(&Subbyte1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subbyte1));
printf("Application.GVL.BYTE2: %d\n", Subbyte1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.WORD3")
{
memcpy(&Subword1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subword1));
printf("Application.GVL.WORD3: %d\n", Subword1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.DWORD4")
{
memcpy(&Subdword1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subdword1));
printf("Application.GVL.DWORD4: %u\n", Subdword1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.LWORD5")
{
memcpy(&Sublword1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Sublword1));
printf("Application.GVL.LWORD5: %ld\n", Sublword1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.SINT6")
{
memcpy(&Subsint1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subsint1));
printf("Application.GVL.SINT6: %d\n", Subsint1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.USINT7")
{
memcpy(&Subusint1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subusint1));
printf("Application.GVL.USINT7: %d\n", Subusint1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.INT8")
{
memcpy(&Subint1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subint1));
printf("Application.GVL.INT8: %d\n", Subint1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.UINT9")
{
memcpy(&Subuint1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subuint1));
printf("Application.GVL.UINT9: %d\n", Subuint1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.DINT10")
{
memcpy(&Subdint1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subdint1));
printf("Application.GVL.DINT10: %d\n", Subdint1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.UDINT11")
{
memcpy(&Subudint1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subudint1));
printf("Application.GVL.UDINT11: %u\n",Subudint1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.LINT12")
{
memcpy(&Sublint1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Sublint1));
printf("Application.GVL.LINT12: %ld\n",Sublint1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.REAL13")
{
memcpy(&Subreal1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Subreal1));
printf("Application.GVL.REAL13: %f\n",Subreal1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.LREAL14")
{
memcpy(&Sublreal1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Sublreal1));
printf("Application.GVL.LREAL14: %lf\n",Sublreal1);
}
else if (std::get<0>(item) == "Application.GVL.STRING15")
{
memcpy(&Substring1, std::get<4>(item).c_str(), sizeof(Substring1));
printf("Application.GVL.STRING15: %s\n",Substring1);
}
}
}
}Principal function
int main()
{
//Read variable
ReadSymbol();
//Write variable
//WriteSymbol();
//Subscribe to variable
//SubSymbol();
return 0;
}Function introduction
1. Declare the client object
/**
* Constructor of Acp Client
*/
AcpClient::AcpClient();2. Connect the server
/**
* @Initialize the Acp Client and establish a connection with the server
* @ parameter in: IP address of the server
* Return value: true for success, and false for failure
*/
bool Init(const std::string& Ip);3. Data structure of read/write variable
/** Input parameter member type of read/write variable
* @param void*: variable type
* @param uint32_t: variable length
*/
using VarPair = std::pair<void*, uint32_t>;
/** Input parameter of read/write variable
* @param std::string: variable address
* @param VarPair: variable type and length
*/
using VarMap = std::map<std::string, VarPair>;4. Read variable
/**
* @brief read variable
* @param in/out: VarMap type
* @param in: timeout
* return: true for success, and false for failure
*/
bool ReadSymbols(const VarMap& symbols,const uint32_t& timeout = 1000);5、Write variable
/**
* @brief write variable
* @param in: VarMap type
* @param in: timeout
* return: true for success, and false for failure
*/
bool WriteSymbols(const VarMap& symbols,const uint32_t& timeout = 1000);6、Register callback function
/**
* @brief
* handler:
* return:
*/
int AcpRemoveNotifyCallBack(TAG_HANDER handler); 7、Add subscription
/**
* @brief
* handler:
* taginfo:
* tagNum:
* nTimeOutMs:
* return:
*/
int AcpAddTagsNotification(TAG_HANDER handler,TagValue* taginfo,
int tagNum,TagSubParam* pSubParam,int nTimeOutMs);- MetaOS Overview
- How to log in and view the system
- How to modify the system language
- How to set network port IP using command line method
- How to set real-time domain system time, non real time domain system time, and hardware time
- How to check the status of PLC
- How to check the status of system resources
- How to view system logs
- How to set system memory
- How to allocate system CPU
- How to allocate system network ports
- How to use the command line to set NIC interrupts
- Chapter 1: Installation and Uninstallation
- Chapter 2: Set the user interface language to Simplified Chinese
- Chapter 3: New Construction
- Chapter 4: Open Project
- Chapter 5: Add / Delete / Export Devices
- Chapter 6: Connecting to PLC
- Chapter 7: Connecting MetaFacture PLC Simulator
- Chapter 8: Downloading and Uploading Projects
- Chapter 9: Scanning Devices
- Chapter 10: Installing and Using Libraries
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Expansion Module
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- SRT3028 | 8 Channel Analog Input Module
- SRT3124 | 4 Channel 0-10V Analog Input Module
- SRT3128 | 8 Channel 0-10V Analog Input Module
- SRT3182 | 2 Channel High-Speed Sampling Module
- SRT3224 | 4 Channel Analog Input Module
- SRT3228 | 8 Channel Analog Input Module
- SRT3324 | 4 Channel Analog Input Module
- SRT3328 | 8 ChannelAnalog Input Module
- SRT3804 | 4 Channel RTD Measurement Module
- SRT3906 | 6 Channel TC Measurement Module
- SRT9xxx | Power Relay Module
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Object Dictionary
- SV35 Profinet Series AC Servo Driver
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product Overview
- Technical Specifications
- Motor