ST1100
Overview
The following table outlines the required components of the product:
| Product Components | Version | Description |
|---|---|---|
| API Function Programming Library Sg.Laser.Framework.SgmcSDK | V1.1 | Used for programming |
| MotionSDK_App.compiled-library | 1.0.7.13 | Lower computer core configuration library |
Installation and Uninstallation
I. Installation Requirements
1. Operating System
Windows 10 or Windows 11 operating system, 64-bit operating system is recommended.
2. Development Platform
Visual Studio 2022 is recommended.
3. Memory
4GB or more.
4. Disk Space
12GB or more.
5. Firewall
It is recommended to turn it off.
II. Installation Process
1. API Function Library Installation Steps
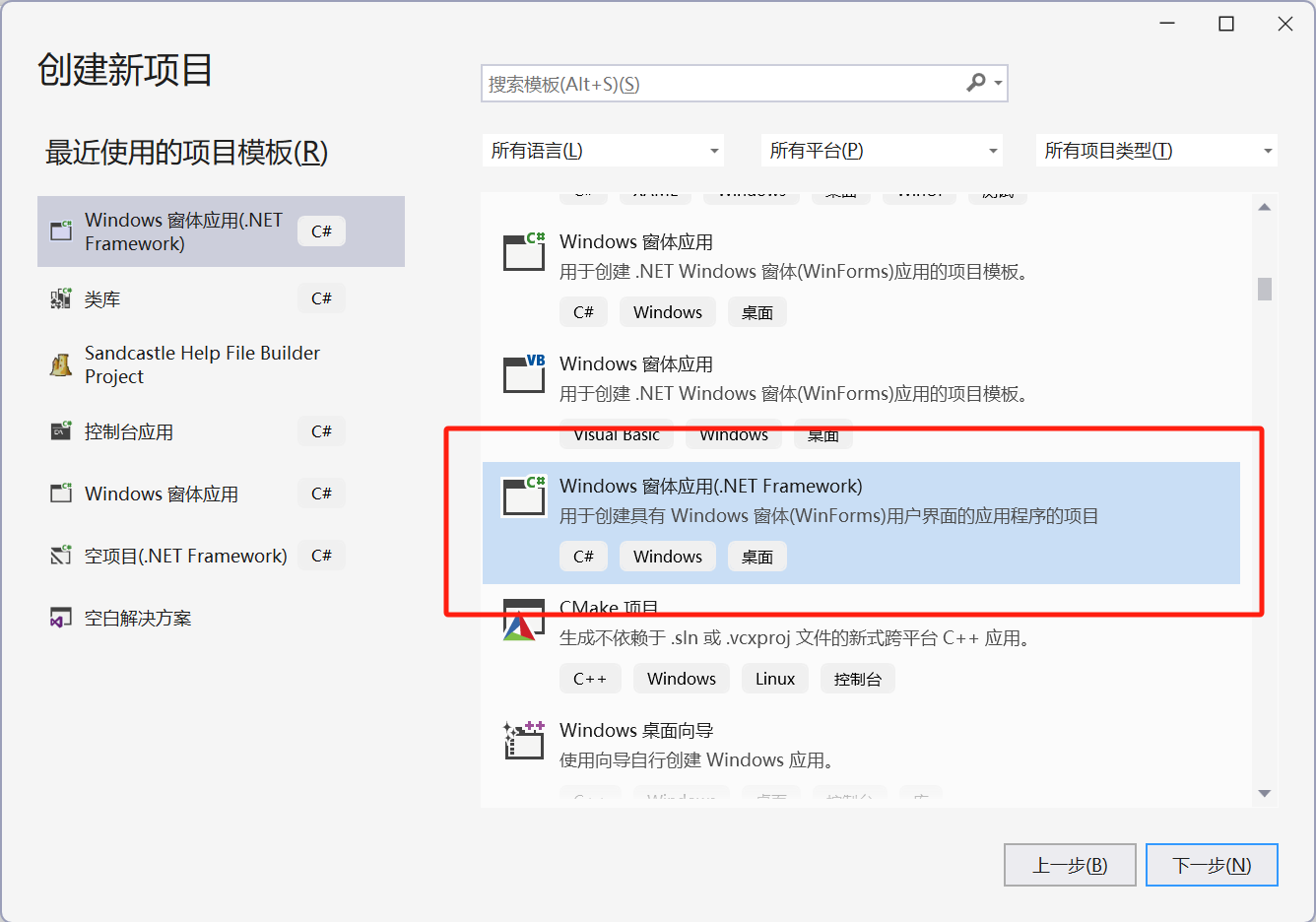
(1) Open Visual Studio 2022, create a new project, select Windows Forms App (.NET Framework), and click "Next" to create it.
(2) Right-click "References" in the solution, select "Add Reference", click Browse, select the API function library: Sg.Laser.Framework.SgmcSDK.dll, and add it.
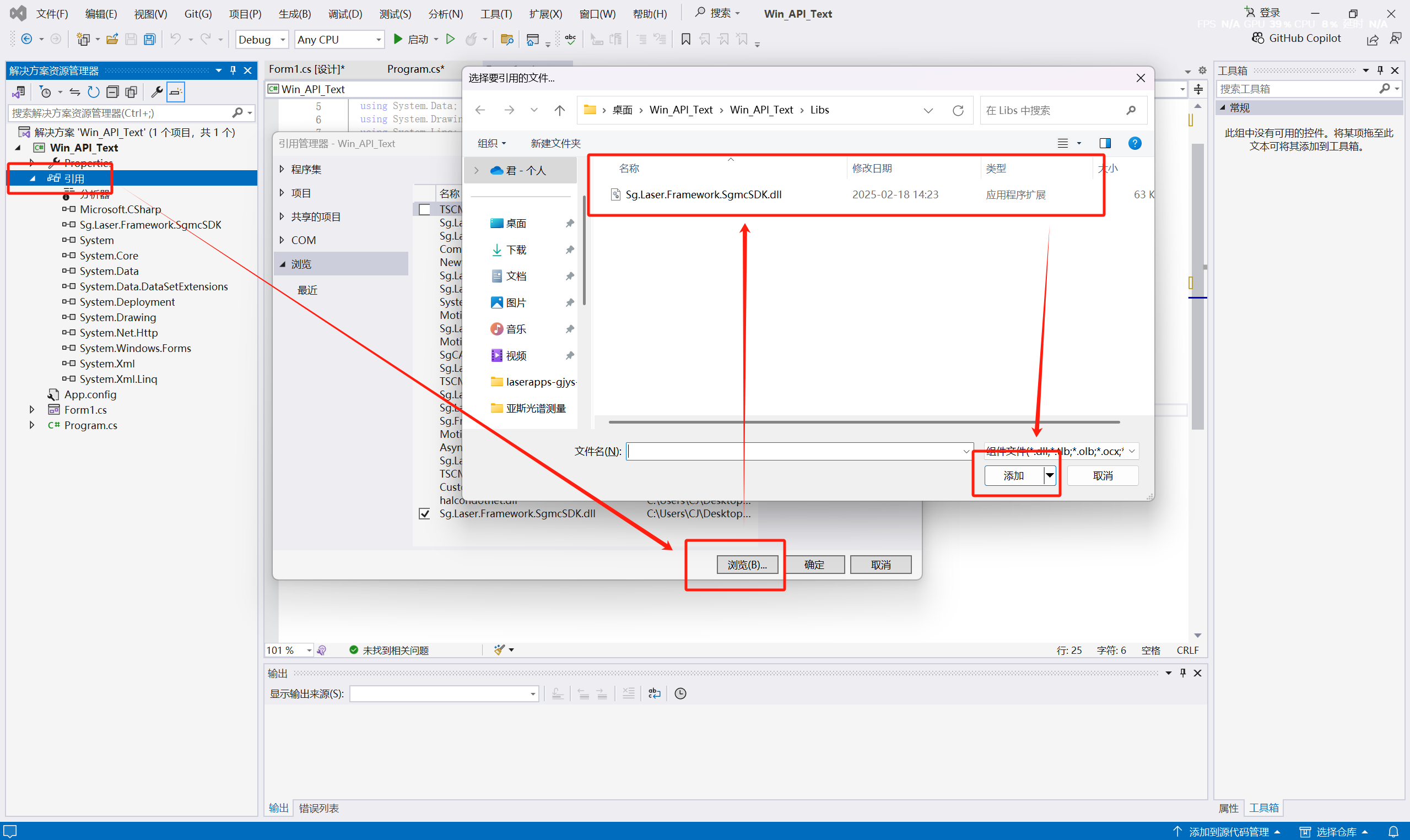
- This completes the configuration of the API function library.
III. Update Installation
| To update the API function library, replace the old version of the library file with the new one and reconfigure it. |
|---|
| For the lower computer library update, reinstall the latest library for the lower computer library storage and configure it. |
IV. Uninstallation Process
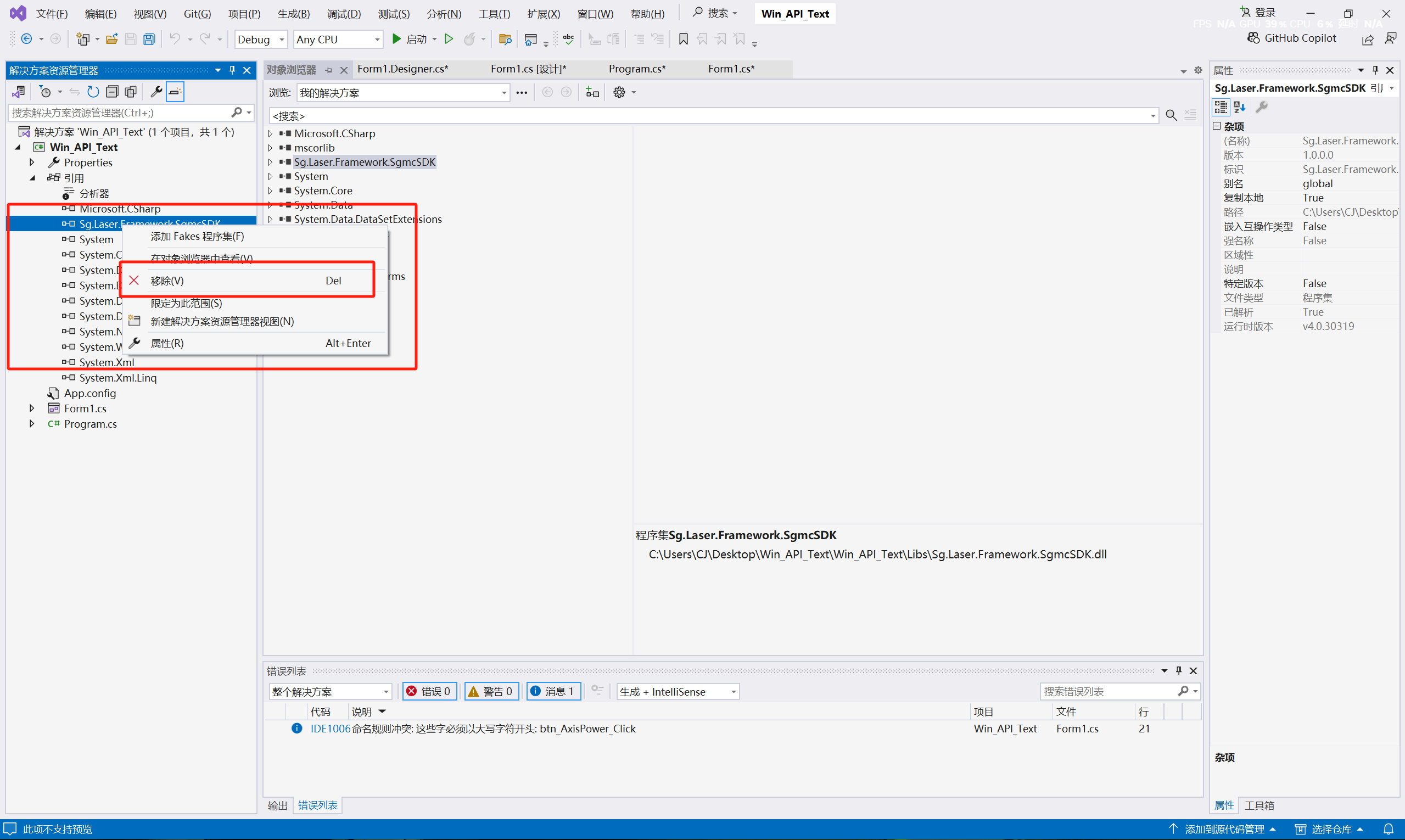
Right-click the reference in the solution, find the API function library, right-click and select "Remove".
Technical Description
I. Quick Start
(I) Software and Hardware Configuration in This Example
| Hardware: 1. iComputer 2. Display (a network cable is needed for laptops) 3. Keyboard and mouse 4. Servo | Software: 1. Visual Studio 2022 2. API library file 3. Lower computer project |
|---|
(II) Experimental Operation Steps of This Example
Testing the case with a laptop:
-
Configure the API function library and the iComputer lower computer project according to the above installation instructions.
-
Prepare a network cable to connect the laptop to the LAN1 port of the iComputer.
-
Open the configured lower computer project, connect to the iComputer and log in.
-
If a servo is prepared, connect the EtherCat interface of the iComputer to the servo; if a virtual axis is used, the status of the corresponding virtual axis can be observed with the lower computer project, and this case uses a virtual axis.
Control Experiment Steps
(1) Open Visual Studio software with the API function library added.
(2) Add a "Button" tool to the Form1 form.
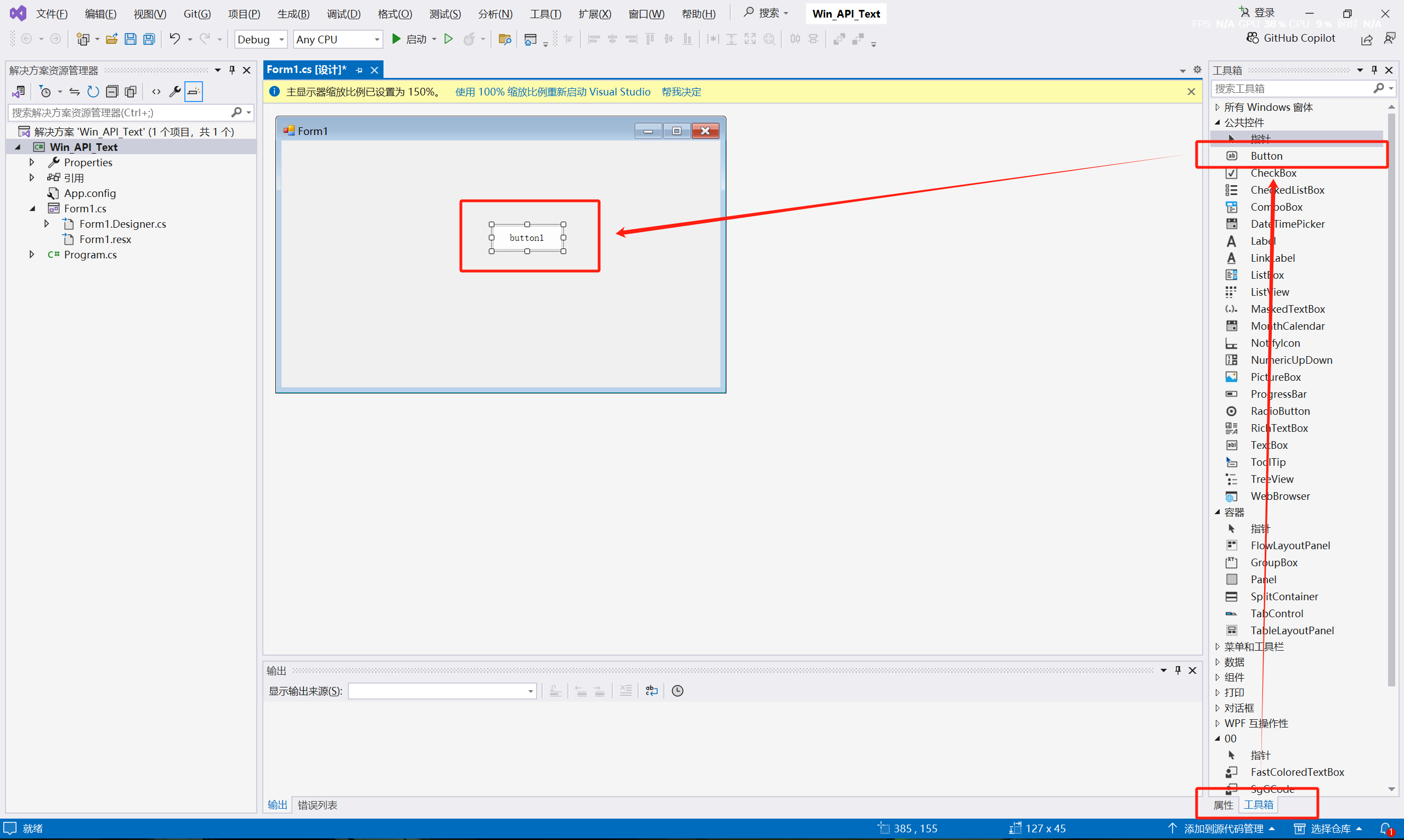
(3) Click Properties, change Text to: Servo Enable, and change (Name) to "btn_AxisPower".
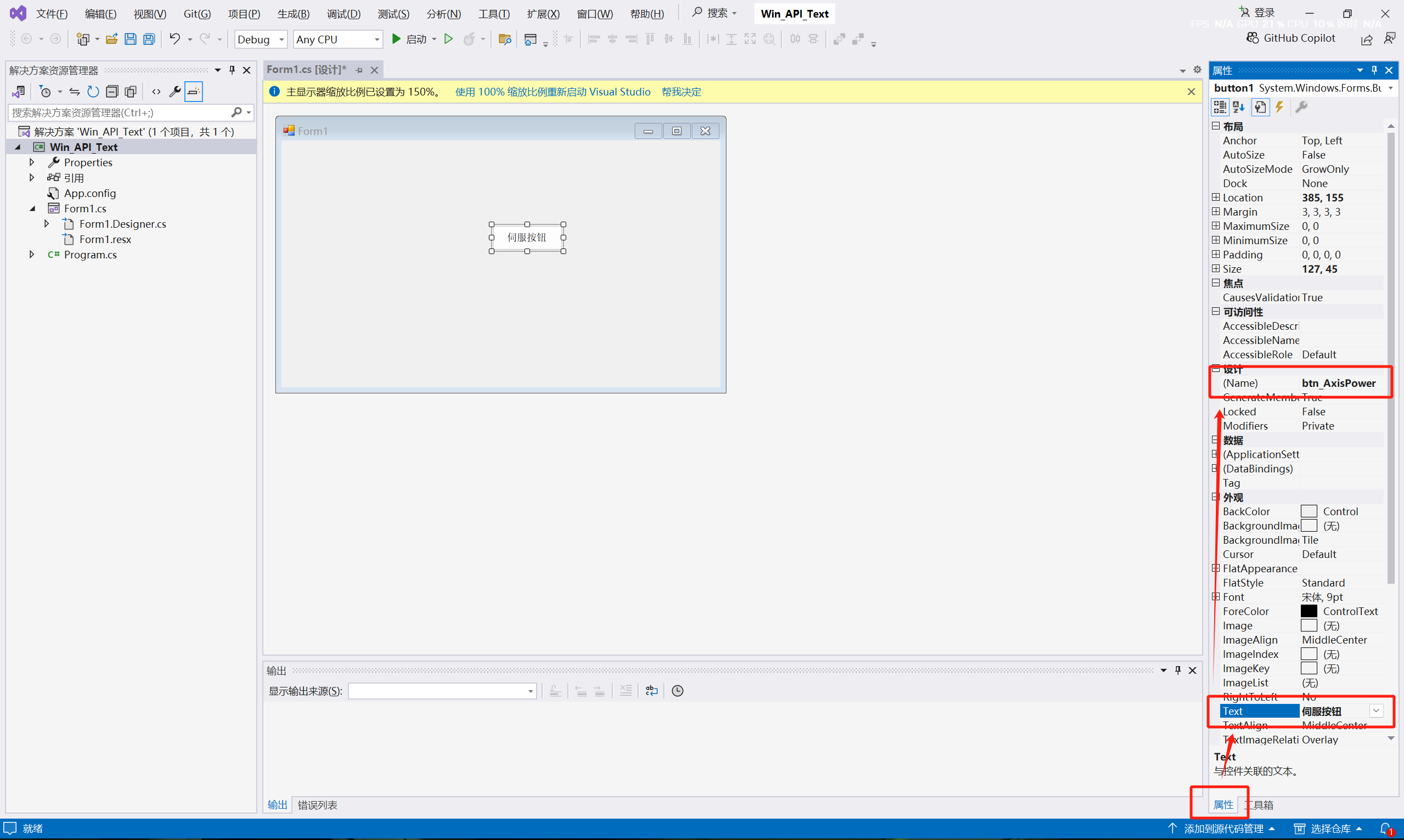
(4) Return to the From1 interface, double-click the "Servo Enable" button with the left mouse button, open the program, and enter the click event editing. Input the API function code: SmcEntity.Instance.Smc_Axis_Enable(0);
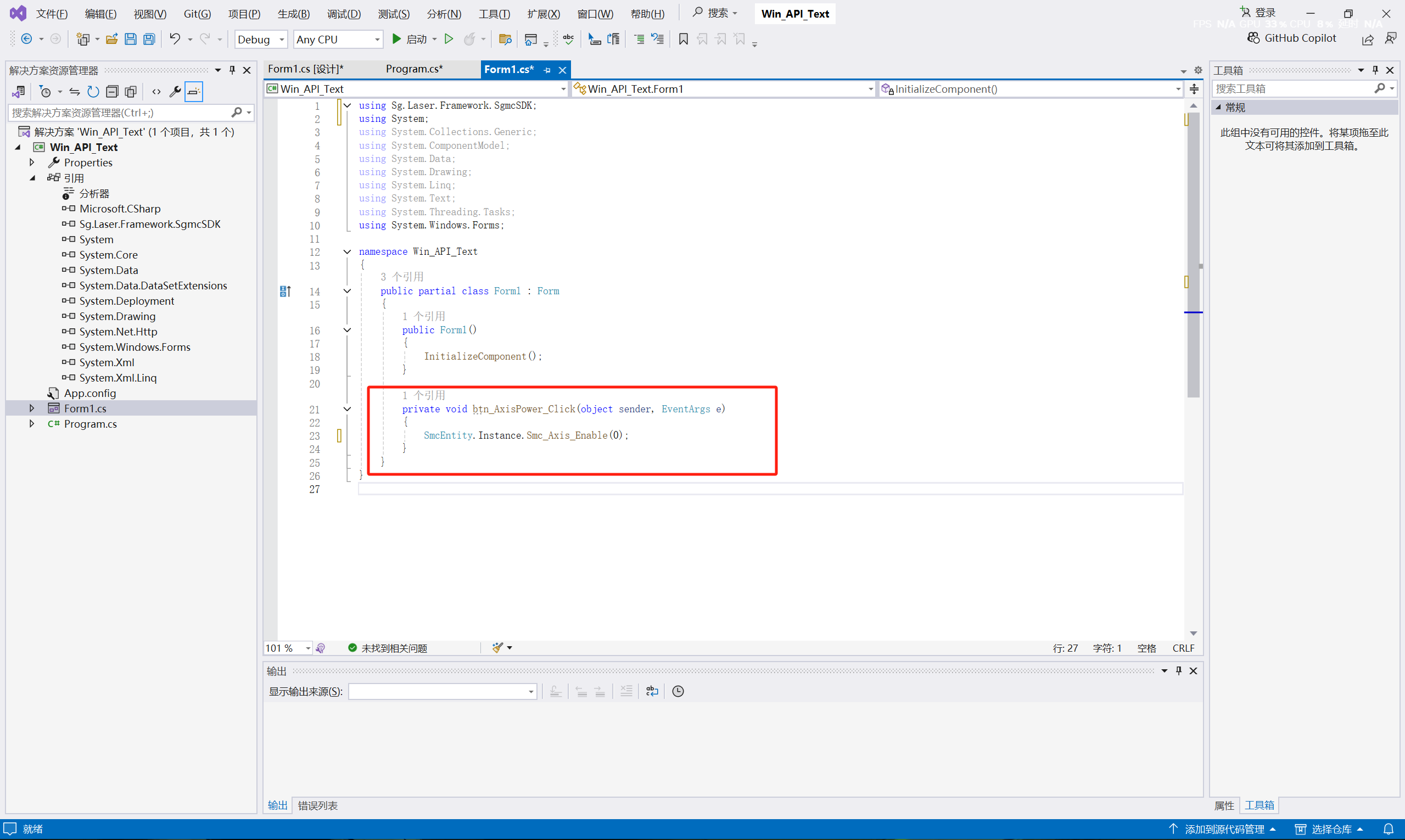
(5) The "0" in SmcEntity.Instance.Smc_Axis_Enable(0) represents axis 0, and the entire instruction represents enabling axis 0.
(6) Return to the main interface, and add a "Connect to iComputer" button according to the above operation of adding the "Servo Enable" button.
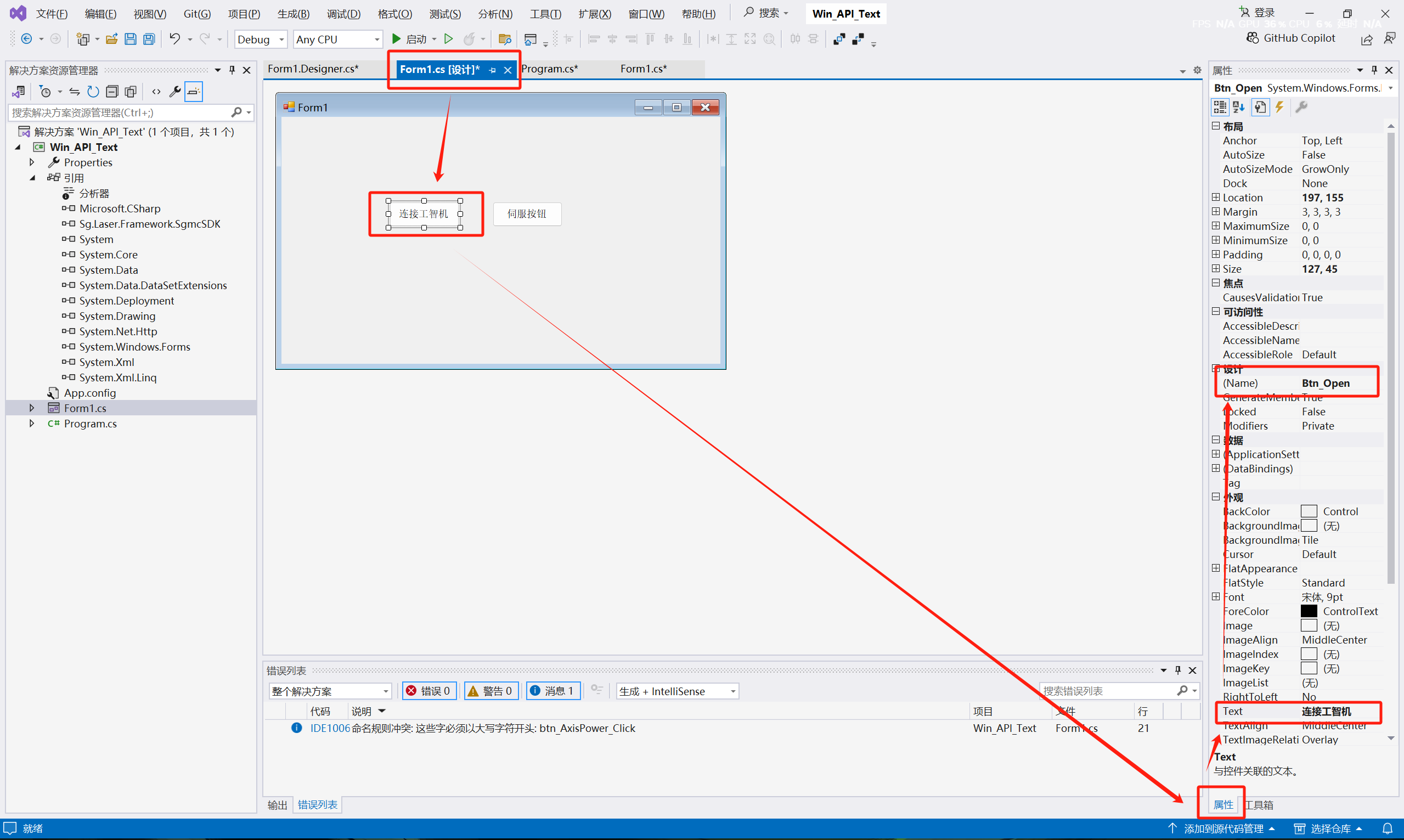
(7) Double-click the button to enter the click event editing, and write the API function:
SmcEntity.Instance.Smc_Open("192.168.1.200",5000); This function is used to communicate with the iComputer through IP and Port.
- Click Start to open the software, left-click the "Connect to iComputer" button, and then click the servo button.
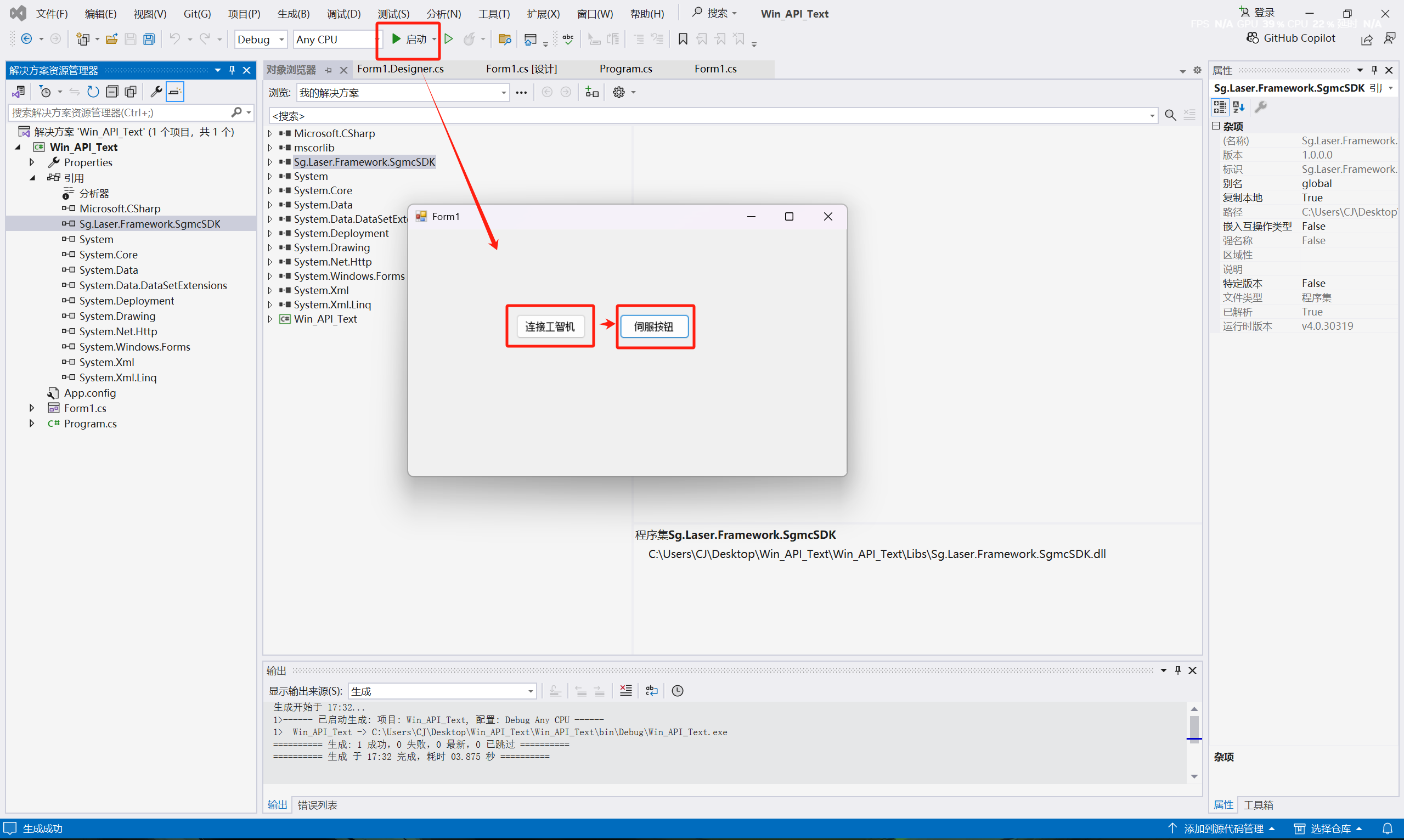
- After completion, observe the status of the virtual axis or the actual servo axis, and you can find that it has become enabled.
(III) Experimental Notes
If you encounter problems during the use of the product, you can refer to here.
1. Click to connect, but cannot connect to the iComputer
Solution:
Check whether the IP port number is set correctly:
The software running on the iComputer, IP: 192.168.3.1, Port: 5000
The software running on the computer, IP: 192.168.1.200, Port: 5000
2. Still cannot connect even if the IP is set correctly
Solution:
(1) Check whether the API lower computer core library file is installed.
(2) Check whether the iComputer is connected.
(3) Whether the lower computer project is configured and logged in to download to the iComputer.
3. Error when clicking the software button
Check whether the API library file is referenced.
II. Examples
The sample code and configuration of this product can be obtained from the link: https://help.sinsegye.com.cn/. Here, you can choose to clone the repository or download the ZlP file containing examples.
The following examples exist:
| Name | Version | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sg.Laser.Framework.SgmcSDK.dll | V1.0.0.4 | API function library file |
| MotionSDK_App.compiled-library | 1.0.7.13 | Lower computer core configuration library |
| Lower computer template project | 18.40 | Programmed lower computer project case |
Function Introduction
I. Controller Initialization
Before operating the motion controller, the function Smc_Init must be called to allocate resources for the motion controller. Similarly, when the program finishes operating the motion controller, the function Smc_Close must be called to release the PC system resources occupied by the motion controller, so that the occupied resources can be used by other devices.
Related functions:
| Name | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smc_Open | Controller connection initialization function | Section 3.1 |
| Smc_Close | Controller closing function |

Note: The controller must be initialized before connecting to it, and the connection method is via network port.
Example 1: Assume the controller IP is "192.168.3.1" and the port number is "5000", connect using UDP communication mode.
Smc_Open("192.168.3.1", 5000);
Example 2: Disconnect.
Smc_Close();
II. Motion Functions
1. Parameter Setting
When the controller executes motion control instructions, it is necessary to set parameters such as the speed, acceleration, deceleration, and jerk of the axis.
Related functions:
| Name | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smc_Set_MoveSpeed | Set single-axis movement speed | Section 3.2 |
| Smc_Get_MoveSpeed | Read single-axis movement speed | |
| Smc_Set_JogSpeed | Set single-axis Jog movement speed | |
| Smc_Get_JogSpeed | Read single-axis Jog movement speed |
Example 1: Set the speed of the 0th axis Move movement to 10mm/s, acceleration to 100mm/s², deceleration to 100mm/s², and jerk to 1000mm/s³:
Smc_Set_MoveSpeed(0,10,100,100,1000);
Example 2: Read the speed vel, acceleration acc, deceleration dec, and jerk of the 0th axis Move movement:
Smc_Get_MoveSpeed(0, ref double vel, ref double acc, ref double dec, ref double jerk);
Example 3: Set the speed of the 0th axis Jog movement to 10mm/s, acceleration to 100mm/s², deceleration to 100mm/s², and jerk to 1000mm/s³: Smc_Set_JogSpeed(0,10,100,100,1000);
Example 4: Read the speed vel, acceleration acc, deceleration dec, and jerk of the 0th axis Jog movement:
Smc_Get_JogSpeed(0, ref double vel, ref double acc, ref double dec, ref double jerk);
2. Point-to-Point Motion
Point-to-point motion includes Jog motion and position motion.
(1) Jog motion refers to: Jog motion, that is, when the button is held down, the motor keeps running, and when the button is released, the motor stops.
In Jog motion mode, each axis can independently set motion parameters such as target speed, acceleration, deceleration, and jerk, and can move or stop independently.
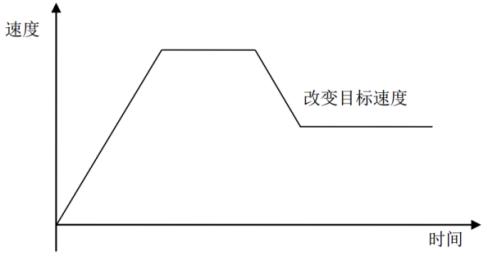
Related functions:
| Name | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smc_MoveJog | Jog motion | Section 3.3 |
Example 1: 0th axis forward Jog motion.
Smc_MoveJog(0, Forward); Example 2: 0th axis reverse Jog motion:
Smc_MoveJog(0, Backward);
(2) Position motion includes relative position motion and absolute position motion.
Relative position motion: Make the axis move a relative distance based on the set speed from the current position and then stop accurately.
Related functions:
| Name | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smc_MoveRelative | Relative position motion | Section 3.3 |
Example: Make the 0th axis move a relative position distance of 10mm at the set speed:
Smc_MoveRelative(0, 10);
Absolute position motion: Make the axis move an absolute position distance based on the set speed from the current position and then stop accurately.
Related functions:
| Name | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smc_MoveAbsolute | Absolute position motion | Section 3.3 |
Example: Make the 0th axis move an absolute position distance of 10mm at the set speed:
Smc_MoveAbsolute(0, 10);
3. Homing Motion
Related functions:
| Name | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smc_GetHomingParameter | Get homing parameters | Section 3.4 |
| Smc_SetHomingParameter | Set homing parameters | Section 3.4 |
Example 1: Get the homing parameters of the 0th axis.
Smc_GetHomingParameter(0, ref Sg_HomingParameter parameter); Example 2: Set the homing parameters of the 0th axis.
Smc_SetHomingParameter(0, Sg_HomingParameter parameter)
| Name | Parameters | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sg_HomingParameter | UsingHoming | Whether to use Homing mode | Section 3.4 |
| fHomePosition | Home position | ||
| fVelocitySlow | Slow speed | ||
| fVelocityFast | Fast speed | ||
| fAcceleration | Acceleration | ||
| fDeceleration | Deceleration | ||
| fJerk | Jerk | ||
| nHomingRefSwitch | Home port number | ||
| nDirection | Homing direction | ||
| nHomingMode | Homing mode |
Example: Make the 0th axis perform homing motion.
Smc_Home_Move(0);
Related functions:
| Name | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smc_Get_Home_Result | Get homing motion status | Section 3.4 |
Example: Get the homing motion status of the 0th axis.
Smc_Get_Home_Result(0,ref state);
III. General IO Functions
1. General IO Control
Users can use the digital I/O ports on the controller to detect input signals such as switch signals and sensor signals, or control output devices such as relays and solenoid valves.
The controller supports IO delay inversion function. After this function is executed, it first outputs a signal opposite to the current level, and then automatically inverts the level again after the set delay time.
The controller supports IO forcing function. After this function is executed, the input/output signal will be forced to the forced value set by the user. General IO control related functions:
| Name | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smc_IO_WriteDO | Set the level state of the output port | Section 3.6 |
| Smc_IO_WriteDO_Flash | Set the flash signal of the output port | |
| Smc_IO_ReadDI | Read the level state of the input port | |
| Smc_IO_SetForceSwitch_DI | Set the forced signal of the input port | |
| Smc_IO_SetForceValue_DI | Set the forced value of the input port | |
| Smc_IO_SetForceSwitch_DO | Set the forced signal of the output port | |
| Smc_IO_SetForceValue_DO | Set the forced value of the output port | |
| Smc_IO_GetDigitIOStatus | Read the status of all digital IO |
Example 1: Set the level state of the 0th output port. Smc_IO_WriteDO(0, 1);
Example 2: Set the flash signal of the 0th output port.
Smc_IO_WriteDO_Flash(0, 1);
Example 3: Read the level state of the 0th input port. Smc_IO_ReadDI(0, ref on_off);
Example 4: Set the forced switch of the 0th input port. Smc_IO_SetForceSwitch_DI(0, 1);
Example 5: Set the forced value of the 0th input port. Smc_IO_SetForceValue_DI(0, 1);
Example 6: Set the forced signal of the 0th output port.
Smc_IO_SetForceSwitch_DO(0, 1);
Example 7: Set the forced value of the 0th output port.
Smc_IO_SetForceValue_DO(0, 1);
Example 8: Read the status of all digital IO.
Smc_IO_GetDigitIOStatus([MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPStr)] StringBuilder info, int size)
IV. CNC Functions
In numerical control machining, the technology of controlling multiple motion axes for interpolation motion simultaneously. This technology enables multiple axes to be controlled simultaneously in complex curve machining, completing the machining task with higher efficiency and more precision.
CNC control related functions:
| Name | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smc_CNC_BeginTransmit | Start downloading | Section 3.7 |
| Smc_CNC_EndTransmit | End downloading | |
| Smc_CNC_Transmit | Download GCode | |
| Smc_CNC_ExecuteReadLine | Upload GCode | |
| Smc_CNC_ExecuteInterpolation | Run | |
| Smc_CNC_PausedInterpolation | Pause | |
| Smc_CNC_ContinueInterpolation | Continue | |
| Smc_CNC_StopInterpolation | Stop | |
| Smc_CNC_Reset | Reset | |
| Smc_CNC_GetProcessingTime | Get CNC processing time | |
| Smc_CNC_GetRobotType | Get robot type | |
| Smc_CNC_SetRobotType | Set robot type | |
| Smc_CNC_GetAxisMapID | Get axis ID | |
| Sgmc_CNC_SetAxisMapID | Set axis ID |
Example 1: Start downloading on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_BeginTransmit(0);
Example 2: End downloading on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_EndTransmit(0);
Example 3: Download GCode on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_Transmit (0, code); //code represents the content of G code
Example 4: Upload GCode on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_ExecuteReadLine (0, ref code); //code represents the content of G code
Example 5: Run on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_ExecuteInterpolation(0);
Example 6: Pause on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_PausedInterpolation(0);
Example 7: Continue on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_ContinueInterpolation(0);
Example 8: Stop on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_StopInterpolation(0);
Example 9: Reset on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_Reset(0);
Example 10: Get CNC processing time on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_GetProcessingTime(0,ref int processingTime )
Example 11: Get robot type on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_GetRobotType(0, ref int RobotType, ref int M_RobotType)
Example 12: Set the robot type of channel 0 to XY type.
Smc_CNC_SetRobotType(0,0) //0: XY type robot; 1: Scara type robot
Example 13: Get axis ID on channel 0.
Smc_CNC_GetAxisMapID(ushort channel, ref int X, ref int Y, ref int Z, ref int A, ref int M_X, ref int M_Y, ref int M_Z, ref int M_A)
Example 14: Set X as axis 0, Y as axis 1, Z as axis 2, and A as axis 3 for channel 0. Sgmc_CNC_SetAxisMapID(0, 0,1, 2, 3)
Function List
I. Communication and Motion Parameters
1. Communication Connection Functions
(1)short Smc_Init(string ipAdress, int ipPort);
Function: Controller connection initialization function, allocating system resources
Parameters: ipAdress specifies the IP address corresponding to the controller, default value 127.0.0.1 ipPort port number, default value 5000
Return value: 0: connection successful, non-zero: connection failure error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
Example: Network port initialization setting
short iret =Smc_Init("192.168.3.103", 5000) //Network port initialization
(2)short Smc_Close()
Function: Controller closing function, releasing system resources Parameters: None
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(3)Short Smc_GetDllVersion([MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPStr)] StringBuilder info, int size)
Function: Get the version number of the controller dynamic library file Parameters: info returns the library version number
size setting size Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
2. Motion Parameter Setting Functions
(1)short Smc_Set_MoveSpeed(ushort axis, double vel, double acc, double dec, double jerk)
Function: Set the speed parameters of Move motion
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 vel speed, unit: mm/s
acc acceleration, unit: mm/s²
dec deceleration, unit: mm/s²
jerk jerk, unit: mm/s³
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(2)short Smc_Get_MoveSpeed(ushort axis, ref double vel, ref double acc, ref double dec, ref double jerk)
Function: Get the speed parameters of Move motion
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1
vel speed, unit: mm/s
acc acceleration, unit: mm/s² dec deceleration, unit: mm/s²
jerk jerk, unit: mm/s³ Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(3)short Smc_Set_JogSpeed(ushort axis, double vel, double acc, double dec, double jerk)
Function: Set the speed parameters of Jog motion
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 vel speed, unit: mm/s
acc acceleration, unit: mm/s²
dec deceleration, unit: mm/s²
jerk jerk, unit: mm/s³ Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(4)short Smc_Get_JogSpeed(ushort axis, ref double vel, ref double acc, ref double dec, ref double jerk)
Function: Get the speed parameters of Jog motion
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 vel speed, unit: mm/s
acc acceleration, unit: mm/s²
dec deceleration, unit: mm/s²
jerk jerk, unit: mm/s³
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
II. Motion Functions
1. Point-to-Point Motion Functions
(1)short Smc_MoveAbsolute( ushort axis, double position )
Function: Absolute position motion
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 position
Position distance, unit: mm
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_MoveRelative(ushort axis, double distance)
Function: Relative position motion
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 distance
Position distance, unit: mm
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_MoveJog(ushort axis, string type)
Function: Jog motion
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1
type Forward: forward rotation, Backward: reverse rotation, Stop: stop
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Check_Done(ushort axis)
Function: Check the completion status of the specified axis
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Stop(ushort axis, ushort stop_mode)
Function: Single-axis stop
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 stop_mode
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Emg_Stop()
Function: Emergency stop all axes
Parameters: None
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
2. Homing Motion Functions
(1)short Smc_Home_Move(ushort axis)
Function: Homing motion
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Get_Home_Result(ushort axis, ref ushort state)
Function: Get homing motion status
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1
state returns homing motion status, 0: not completed, 1: completed
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- Smc_GetHomingParameter(ushort axis, ref Sg_HomingParameter parameter)
Function: Get homing parameters
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 parameter returns specific homing parameters,
UsingHoming: whether to use Homing mode fHomePosition: home position
fVelocitySlow: slow speed fVelocityFast: fast speed fAcceleration: acceleration fDeceleration: deceleration fJerk: jerk
nHomingRefSwitch: home port number
nDirection: homing direction nHomingMode: homing mode
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- Smc_SetHomingParameter(ushort axis, Sg_HomingParameter parameter)
Function: Set homing parameters
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 parameter returns specific homing parameters,
UsingHoming: whether to use Homing mode fHomePosition: home position
fVelocitySlow: slow speed fVelocityFast: fast speed fAcceleration: acceleration
fDeceleration: deceleration fJerk: jerk
nHomingRefSwitch: home port number
nDirection: homing direction nHomingMode: homing mode
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
3. Status Monitoring Functions
(1)short Smc_GetAxisState([MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPStr)] StringBuilder axisState, int size)
Function: Get the status of motion-related signals of the specified axis
Parameters: axisState returns the status of motion-related signals of the axis size setting size
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Get_PowerStatus(ushort axis, ref ushort state)
Function: Get the enable status of the specified axis
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1
state returns enable status, 0: not enabled, 1: enabled
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Set_Position(ushort axis, double pos)
Function: Set the current position of the specified axis
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1
pos position, unit: mm
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Get_ActPosition(ushort axis, ref double pos)
Function: Get the actual position of the specified axis
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 pos returns actual position, unit: mm
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Get_TargetPosition(ushort axis, ref double pos)
Function: Get the planned position of the specified axis
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 pos returns planned position, unit: mm
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Get_ActVelocity(ushort axis, ref double speed)
Function: Get the actual speed of the specified axis
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1
speed returns actual speed, unit: mm/s
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_Get_ActAcceleration(ushort axis, ref double actacc)
Function: Get the actual acceleration of the specified axis
Parameters: axis axis number, range: 0 ~ maximum axis number of the controller -1 actacc returns actual acceleration, unit: mm/s²
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
III. IO Functions
1. General IO Interface Functions
(1)int Smc_IO_ReadDO(ushort bitno, ref ushort on_off);
Function: Read the signal status of the specified output port
Parameters: bitno output port number, range: 0 ~ number of local output ports of the controller -1
on_off output port signal, 0: low level, 1: high level
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_IO_WriteDO(ushort bitno, ushort on_off)
Function: Set the signal of the specified output port
Parameters: bitno output port number, range: 0 ~ number of local output ports of the controller -1 on_off output port signal, 0: low level, 1: high level
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_IO_WriteDO_Flash(ushort bitno, ushort on_off)
Function: Set the flash signal of the specified output port
Parameters: bitno output port number, range: 0 ~ number of local output ports of the controller -1
on_off output port signal
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_IO_ReadDI(ushort bitno, ref ushort on_off)
Function: Get the input port signal
Parameters: bitno input port number, range: 0 ~ number of local output ports of the controller -1
on_off returns input port signal
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_IO_SetForceSwitch_DI(ushort bitno, ushort on_off)
Function: Set the forced signal of the input port
Parameters: bitno input port number, range: 0 ~ number of local output ports of the controller -1 on_off input port forced signal
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_IO_SetForceValue_DI(ushort bitno, ushort on_off)
Function: Set the forced value of the input port
Parameters: bitno input port number, range: 0 ~ number of local output ports of the controller -1 on_off input port forced value
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_IO_SetForceSwitch_DO(ushort bitno, ushort on_off)
Function: Set the forced signal of the output port
Parameters: bitno output port number, range: 0 ~ number of local output ports of the controller -1 on_off output port forced signal
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_IO_SetForceValue_DO(ushort bitno, ushort on_off)
Function: Set the forced signal of the output port
Parameters: bitno output port number, range: 0 ~ number of local output ports of the controller -1 on_off output port forced value
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- short Smc_IO_GetDigitIOStatus([MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPStr)]StringBuilder info, int size)
Function: Get the status of digital IO
Parameters: info returns IO status size setting size
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
2. Analog IO Interface Functions
(1)int Smc_IO_ReadAO(ushort bitno, ref double value);
Function: Read analog output
Parameters: bitno IO point Value analog voltage value
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(2)int Smc_IO_WriteAO (ushort bitno, double value);
Function: Write analog output
Parameters: bitno IO point Value analog output voltage value
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(3)int Smc_IO_SetForceSwitch_AO(ushort bitno, ushort on_off);
Function: Set analog forced output switch
Parameters: bitno forced IO point
on_off forced enable signal
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(4)int Smc_IO_SetForceValue_AO(ushort bitno, double value);
Function: Set analog forced output value
Parameters: bitno forced IO point
Value forced value
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
3. Special IO Functions
(1)int MoveAbsoluteAndMemOutIO(int axisID, float position, int percent, int port);
Function: Absolute motion synchronous output memory signal
Parameters: axisID axis number
position target position
percent proportion of motion path to trigger signal
port port to trigger memory signal
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(2)int Smc_IO_WriteMemIO(ushort bitno, ushort on_off);
Function: Write memory bit IO
Parameters: bitno IO port number on_off switch
Note: This signal can be operated after the motion is triggered
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(3)int Smc_IO_ReadMemIO(ushort bitno, ref ushort on_off);
Function: Read memory bit IO
Parameters: bitno IO port number on_off signal status
Note: This signal can be operated after the motion is triggered
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(4)int Smc_IO_WriteDO_PWM(ushort bitno, ushort on_off, int frequency, int dutyfactor);
Function: Write PWM signal
Parameters: bitno PWM type IO port number on_off on or off
frequency pulse width signal period dutyfactor duty cycle
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(5)int Smc_IO_WriteDO_PSO(ushort bitno, ushort on_off, int OutputDelay, float StartPos, float TrigDist, int PSO_AxisNum);
Function: Write PSO signal
Parameters: bitno PSO type IO port number on_off on or off
OutputDelay duration after the signal is turned on StartPos start position to trigger the signal
TrigDist trigger distance setting
PSO_AxisNum PSO signal participating axis number setting, range 1-3. When set to 1, the start position and trigger distance are only related to the first axis corresponding to the configuration in the lower computer parameters
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
IV. Limit Functions and CNC Functions
1. Soft Limits
(1)int Smc_SetSoftwareLimits(int axisID, double limitPositive, double limitNegative);
Function: Set software limits
Parameters: axisID axis number
limitPositive positive limit limitNegative negative limit
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(2)int Smc_ActivateSoftwareLimits(int axisID, ushort bActivate);
Function: Activate software limits
Parameters: axisID axis number
bActivate whether to activate
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(3)int Smc_GetSoftwareLimits(int axisID, ref ushort bActivate, ref double limitPositive, ref double limitNegative);
Function: Get software limits
Parameters: axisID axis number
bActivate whether to activate
limitPositive positive limit limitNegative negative limit
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
2. CNC Control Related Functions
(1)Smc_CNC_BeginTransmit(ushort channel)
Function: Start downloading GCode
Parameters: channel channel
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(2)Smc_CNC_EndTransmit(ushort channel)
Function: End downloading GCode
Parameters: channel channel
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(3)Smc_CNC_Transmit(ushort channel, string code)
Function: Download GCode
Parameters: channel channel
code G code content
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(4)Smc_CNC_ExecuteReadLine(ushort channel, ref string code)
Function: Upload GCode
Parameters: channel channel code G code content
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(5)Smc_CNC_ExecuteInterpolation(ushort channel)
Function: Run GCode
Parameters: channel channel
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(6)Smc_CNC_ExecuteInterpolation(ushort channel)
Function: Run GCode
Parameters: channel channel
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(7)Smc_CNC_PausedInterpolation(ushort channel)
Function: Pause running GCode
Parameters: channel channel
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(8)Smc_CNC_ContinueInterpolation(ushort channel)
Function: Continue running GCode
Parameters: channel channel
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(9)Smc_CNC_StopInterpolation(ushort channel)
Function: Stop running GCode
Parameters: channel channel
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(9)Smc_CNC_Reset(ushort channel)
Function: Reset
Parameters: channel channel
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(10)Smc_GetCardStatus(ref Sg_CardStatus cardStatus, ref Sg_CNC_State cncstatus0, ref Sg_CNC_State cncstatus1)
Function: Get board status
Parameters: cardStatus board status, cncstatus0 CNC0 status, cncstatus1 CNC1 status
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(11)Smc_CNC_GetProcessingTime(ushort channel, ref int processingTime)
Function: Get CNC processing time
Parameters: channel channel, processingTime processing time
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(12)Smc_CNC_GetRobotType(ushort channel, ref int RobotType, ref int
M_RobotType)
Function: Get robot type
Parameters: channel channel, RobotType, M_RobotType: robot type
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(13)Smc_CNC_ SetRobotType(ushort channel, int RobotType)
Function: Set robot type
Parameters: channel channel, RobotType: robot type
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(14)Smc_CNC_GetAxisMapID(ushort channel, ref int X, ref int Y, ref int Z, ref int A, ref int M_X, ref int M_Y, ref int M_Z, ref int M_A)
Function: Get axis map ID
Parameters: channel channel axis numbers: X, Y, Z, A, M_X, M_Y, M_Z, M_A
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(15)Sgmc_CNC_SetAxisMapID(ushort channel, int X, int Y, int Z, int A)
Function: Set axis map ID
Parameters: channel channel, axis numbers: X,Y,Z,A
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
3. Other Functions
(1)Smc_GetEncoderIn(ushort channel, ref int outvalue, ref double
realvalue)
Function: Get the value of the external encoder
Parameters: channel channel,
outvalue: actual output value, realvalue: offset internal output value
Return value: Error code
Applicable range: All series of controllers
(2)Smc_SetEncoderOffset(ushort channel, int pos)
Function: Set the value of the external encoder
Return value: Error code
Parameters: channel channel, pos: position
Applicable range: All series of controllers
- MetaOS Overview
- How to log in and view the system
- How to modify the system language
- How to set network port IP using command line method
- How to set real-time domain system time, non real time domain system time, and hardware time
- How to check the status of PLC
- How to check the status of system resources
- How to view system logs
- How to set system memory
- How to allocate system CPU
- How to allocate system network ports
- How to use the command line to set NIC interrupts
- Chapter 1: Installation and Uninstallation
- Chapter 2: Set the user interface language to Simplified Chinese
- Chapter 3: New Construction
- Chapter 4: Open Project
- Chapter 5: Add / Delete / Export Devices
- Chapter 6: Connecting to PLC
- Chapter 7: Connecting MetaFacture PLC Simulator
- Chapter 8: Downloading and Uploading Projects
- Chapter 9: Scanning Devices
- Chapter 10: Installing and Using Libraries
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Expansion Module
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product overview
- Technical Specifications
- Troubleshooting and Disposal
- Care and Maintenance
- Appendix
- SRT3028 | 8 Channel Analog Input Module
- SRT3124 | 4 Channel 0-10V Analog Input Module
- SRT3128 | 8 Channel 0-10V Analog Input Module
- SRT3182 | 2 Channel High-Speed Sampling Module
- SRT3224 | 4 Channel Analog Input Module
- SRT3228 | 8 Channel Analog Input Module
- SRT3324 | 4 Channel Analog Input Module
- SRT3328 | 8 ChannelAnalog Input Module
- SRT3804 | 4 Channel RTD Measurement Module
- SRT3906 | 6 Channel TC Measurement Module
- SRT9xxx | Power Relay Module
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Object Dictionary
- SV35 Profinet Series AC Servo Driver
- Safety tips for unpacking acceptance
- Safety tips for storage and transport
- Safety tips during assembly
- Safety tips for equipment wiring
- Safety tips for equipment power-on
- Safety tips for equipment operation
- Safety tips for equipment maintenance
- Safety tips for equipment repair
- Safety tips for equipment recycling
- Product Overview
- Technical Specifications
- Motor